|
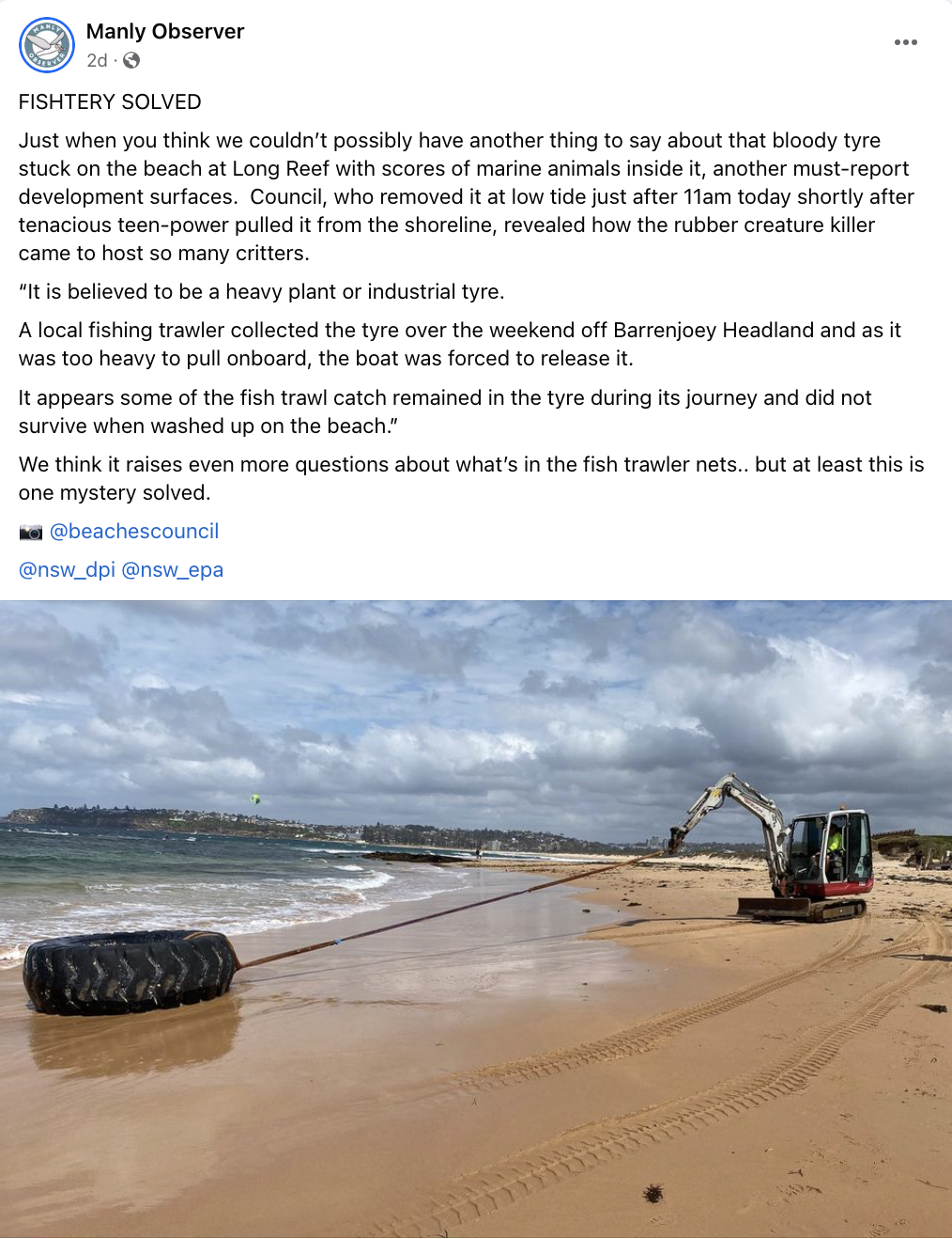
Over the last couple of weeks, the Manly Observer has been recording the appearance and removal of an industrial tyre at Long Reef and the actions of mostly young people in the community to relocate it. They removed the sand that had built up inside it to try to make it easier to move, but each time they took out a layer of sand they found a variety of fish, rays and juvenile sharks. In all, around 80 marine creatures were removed from the inside of the tyre. Read the full story here: How 80 dead creatures came to rest inside an industrial tyre on the Long Reef Shoreline The reporters and community engaged in discussions about how so many marine creatures could have made their way inside the tyre. Some suggested that it was being used for shelter, and then as the tides went out animals became trapped. Eventually the group managed to move the tyre away from the shoreline, and it drew enough attention that the local council became involved the remove it from the beach entirely. Council reported that a local fishing trawler had let them know that they had unintentionally pulled up the tyre out of the water, but it was too weighty to bring aboard the ship, and they released it back into the water. The creatures inside the tyre were most likely to have been bycatch, caught in the trawlers net.
This is a great little story to use in the classroom. Active Citizenship It highlights the importance of active citizenship in the most practical way. It shows that how young people can have an impact on their environment, work collaboratively and achieve something tangible that initially seems beyond their capacity. It demonstrates how collective action can get the attention of media, government and the community and bring about more change than the individuals are capable of by themselves. Geographic Investigation This story is a great way to talk to students about hypotheses, assumptions, using sources, and drawing conclusions. The teenagers began their own investigation of the tyre, found the dead creatures and assumed the tyre had caused the deaths. The tyre may have caused some of those deaths. The idea of fish getting caught on the low tide is entirely plausible, but doesn’t seem to account for the huge number of creatures found. Regardless, I love that some mostly incorrect assumptions resulted in these teenagers doing something great (removing rubbish from our oceans). Contacting additional sources – like the local council - led to the alternate and more plausible explanation of the involvement of the fishing trawler. Let’s hope these young people are now encouraged to find out more about trawling. Problem Solving and Mystery The way this story unfolded on social media was really interesting and engaging, and this could be replicated in a classroom by only providing some pieces of information at a time and allowing students to problem solve and eventually solve a mystery. Students could be presented with a range of scenarios to explore - the tyre in the water, the creatures in the tyre, the weight of the tyre, the encroaching tide, etc. Student could be asked to problem solve each step and be given roadblocks or positive outcomes dependent on the solution they come up with. Open ended questions could be provided to encourage deeper exploration of coastal environments, environmental issues and management strategies. The structure could almost be set up like a murder mystery, with clues along the way, and students trying to solve the crime. It is easy to fall into a trap of thinking that environmental issues are too big for an individual to have an impact. I have only recently had some conversations with students who felt they couldn’t make any real impact because the world’s problems were just too big. This is a great, short story to engage students with geography and show the impact that individuals and groups can have their local environment, but also that once that first job is one, there’s more to do!
0 Comments
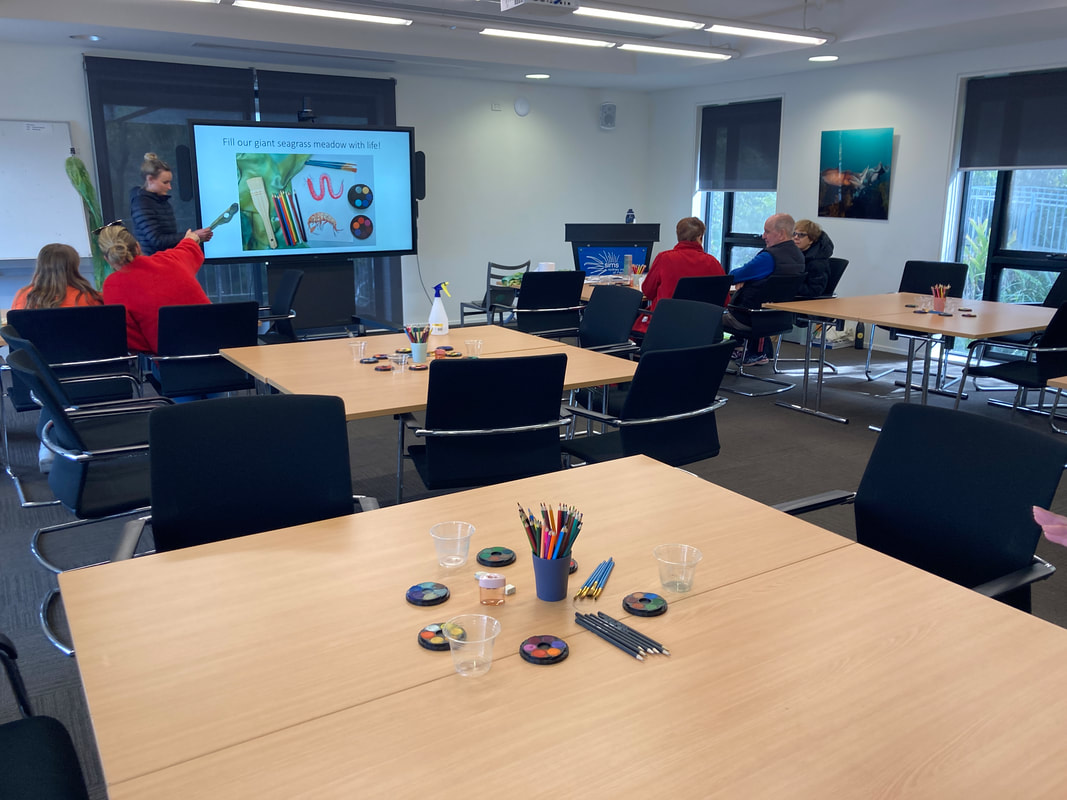
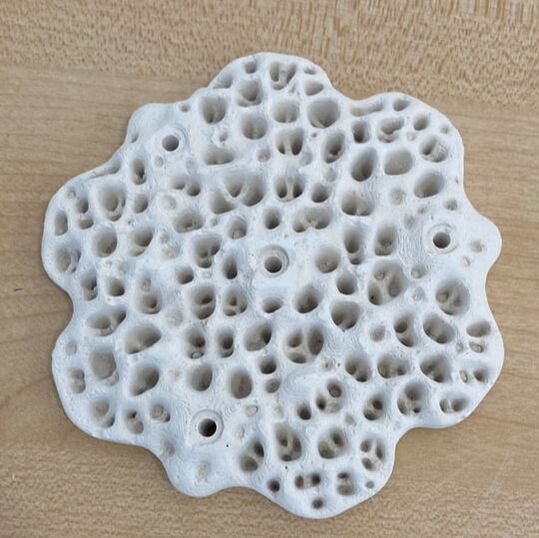
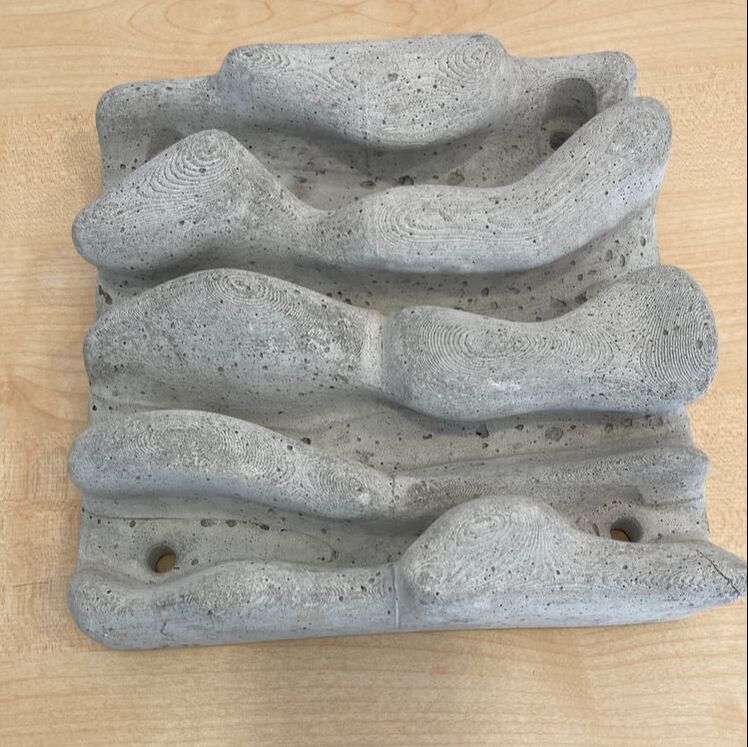
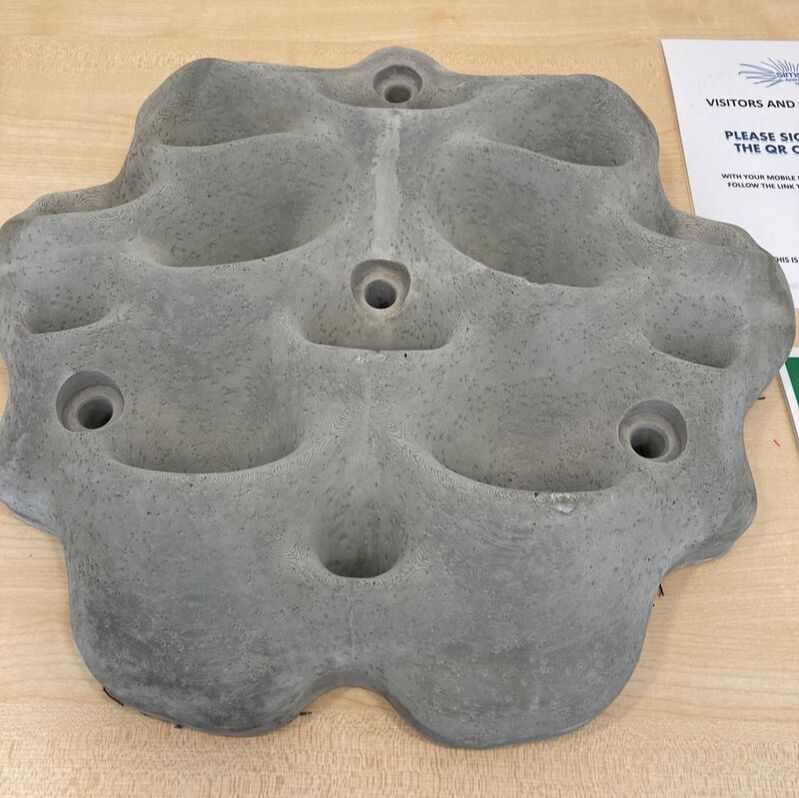
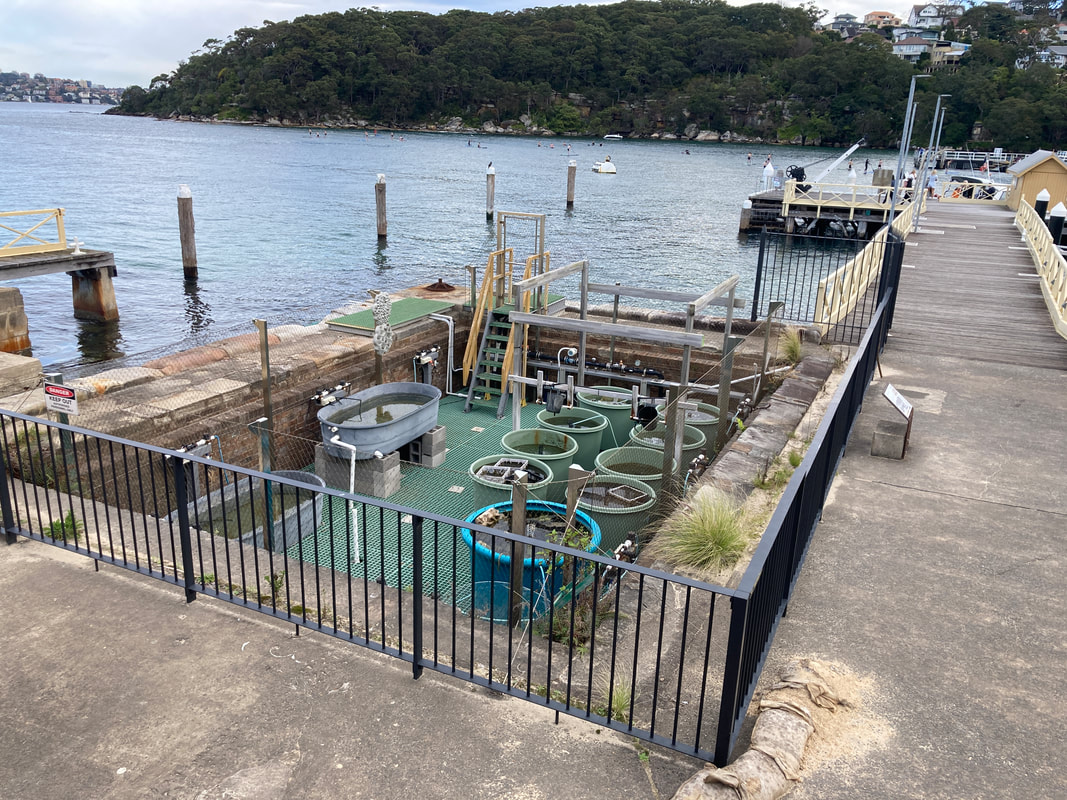
This week we picked up some Living Seawall panels to install on school property as part of the Balmain Foreshore Project. A section of our school property, along the water’s edge allows public access to the Bay Walk and is a thoroughfare accessed by members of the public. The project provides a unique opportunity for our school to contribute to environmental sustainability, teach students about their community responsibilities, and inform the public about environmental issues affecting the local community. As part of this project, earlier in the year, students heard from the Aria Lee, Project Manager of Living Seawalls who told students about the research and development behind the concept of Living Seawalls, the locations where they can be found around Sydney Harbour and globally, and the ecological benefits of Living Seawalls. A few months ago our Balmain Foreshore Project team was excited to receive a substantial Westconnex Community Grant for continuation of the Balmain Foreshore Project. As part of the Westconnex Grant, funds have been allocated to purchase and install Living Seawall panels on the seawall on school property in an attempt to improve water quality and encourage greater biodiversity in the local waterway. Prior to installation we will be collecting baseline data to identify the diversity of species currently inhabiting the seawall, and we intend to set up a longitudinal study to investigate change over time in species diversity.
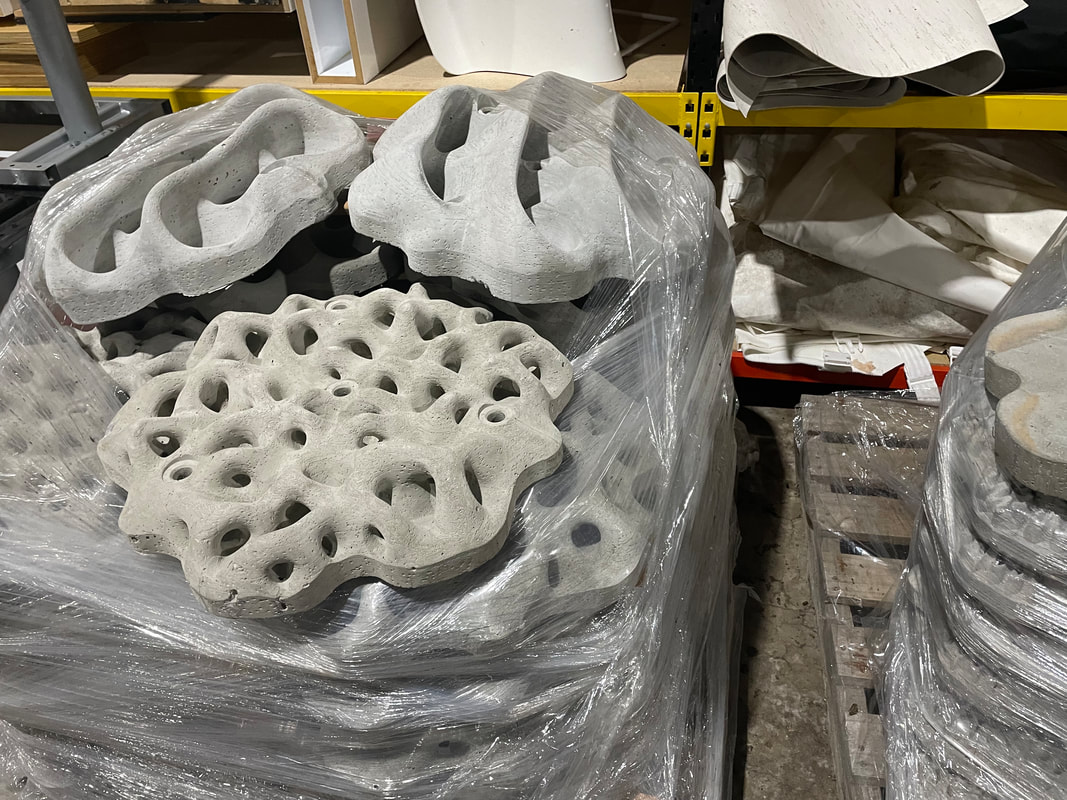
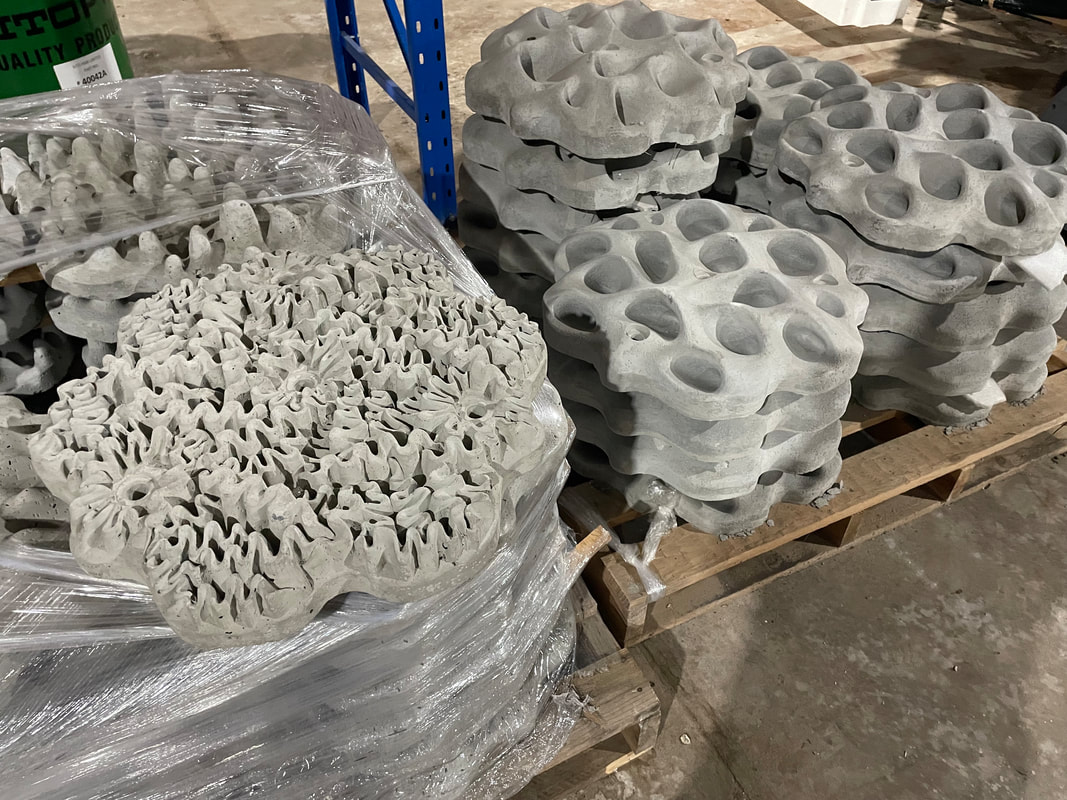
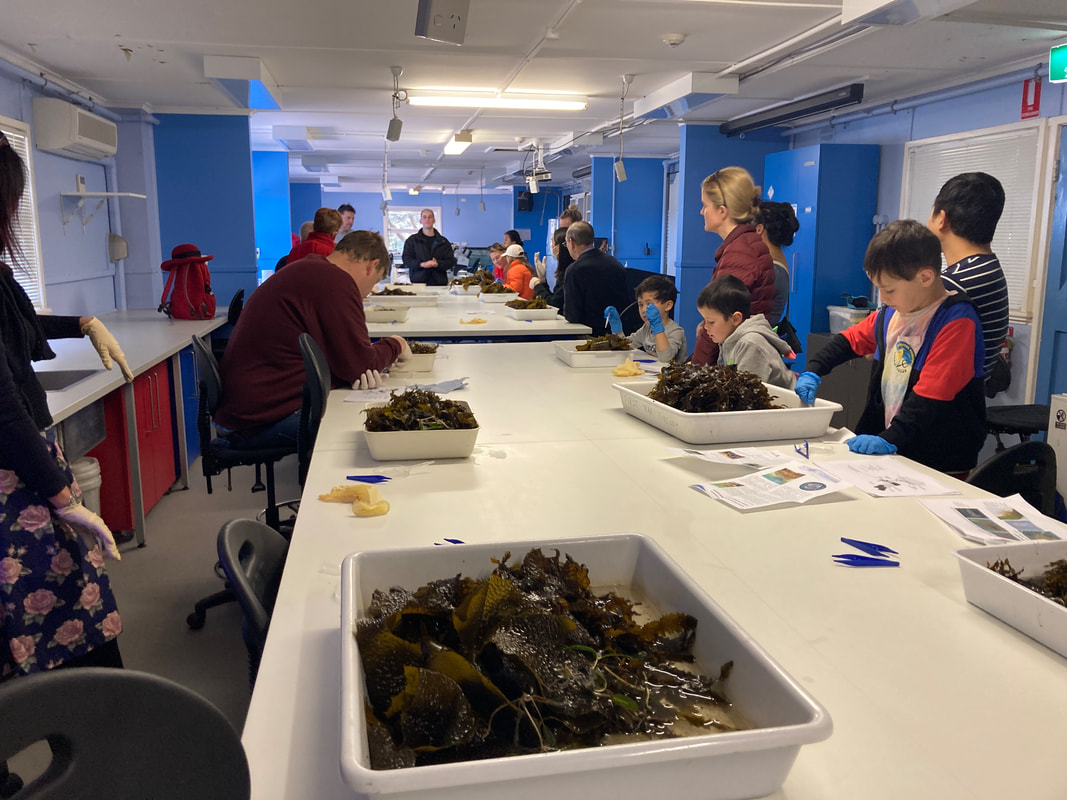
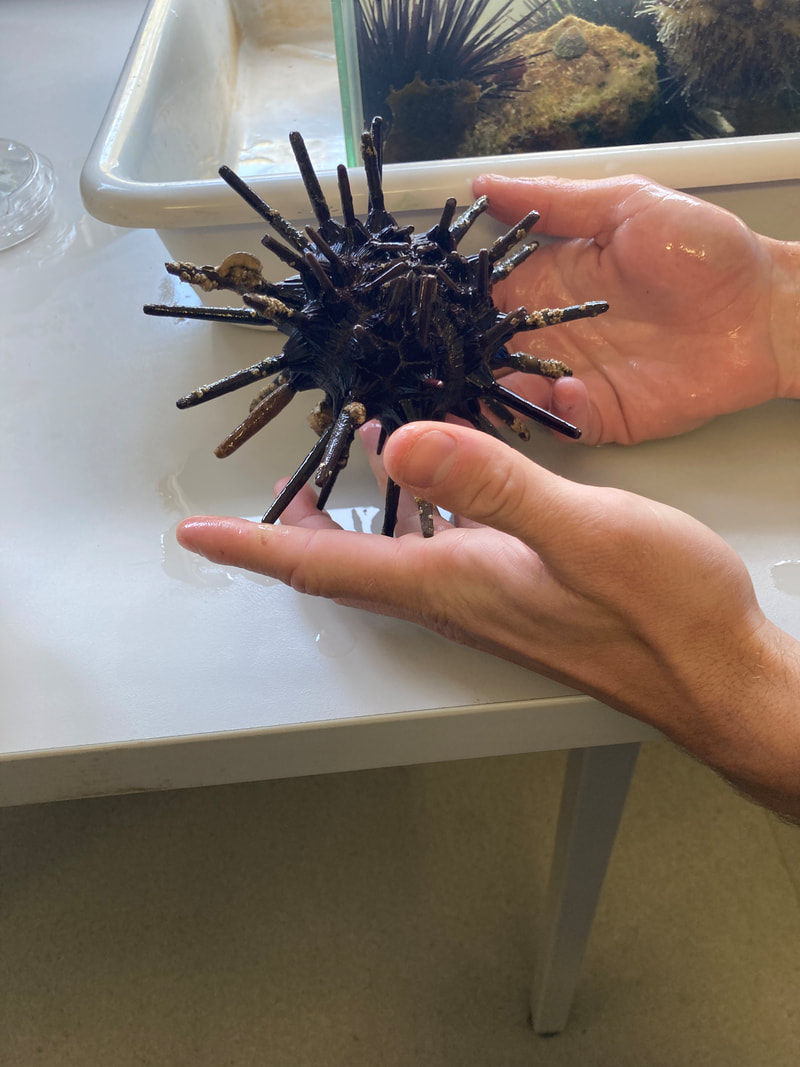
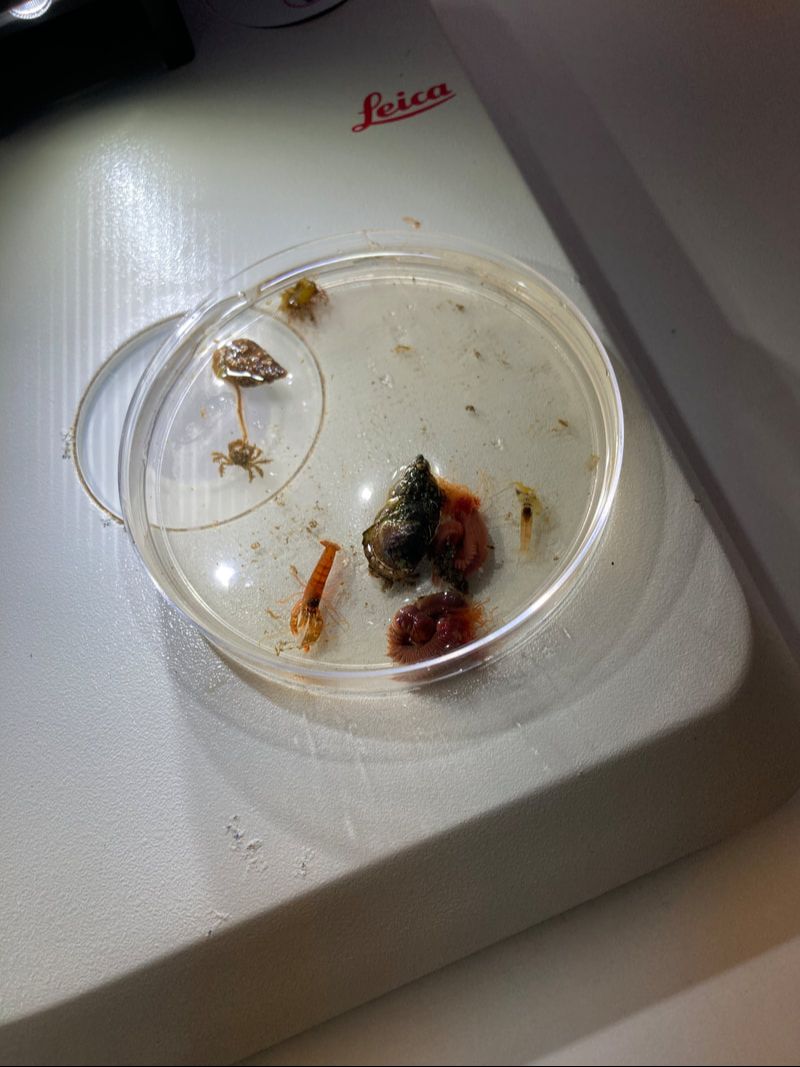
This is one of several posts about our Balmain Foreshore Project. Read more... Balmain Foreshore Project - Introduction Gardening Below the Surface - Operation Posidonia Balmain Foreshore Project - Trial Activities Balmain Foreshore Project - Implementation Balmain Foreshore Project - Living Seawalls Balmain Foreshore Project - Living Seawalls: Pre-Installation Biodiversity Survey As part of National Science Week, the Sydney Institute of Marine Science (SIMS) held sessions to raise public awareness about the fragile nature of seagrass meadows. Although this event was promoted as a Science event, it had clear links to the Geography syllabus - both the Year 10 Environmental Change and Management topic and the Year 9 - Biomes topic. SIMS is located on Chowder Bay Rd, Mosman. The session involved examining specimens form nearby Chowder Bay/Clifton Gardens, a tour of classroom facilities and a display of seawall panel designs. As information on the Great Southern Reef becomes more readily available, some of these activities would tie in really well with this case study of Geography classes. Seagrass and seaweed - there was a collection aquatic organisms which could be identified using a field chart and also facilities to exam them under the microscope Part of the day involved an art project to promote public awareness about seagrass. The artworks were transferred onto silks that had been dyed to represent seagrass. This became part of an installation at Mosman Art Gallery. You can read more about the art project here: https://www.lissfinney.com/public-projects There was also a display of seawall panels designed by Living Seawalls. These panels are designed to be adhered to seawalls to encourage biodiversity. The crevices are intended to encourage aquatic species to use the structure as habitat. You can read about Living Seawalls here: https://www.livingseawalls.com.au/ There is a testing area where the Living Seawall panels are being tested in Chowder Bay. The shark nets at this site are also a common place for snorkelers to find seahorses.
I'm definitely coming back for a closer look. This is one of several posts about our Balmain Foreshore Project. Read more... Balmain Foreshore Project - Introduction Gardening Below the Surface - Operation Posidonia Balmain Foreshore Project - Trial Activities Balmain Foreshore Project - Implementation Balmain Foreshore Project - Living Seawalls Balmain Foreshore Project - Living Seawalls: Pre-Installation Biodiversity Survey
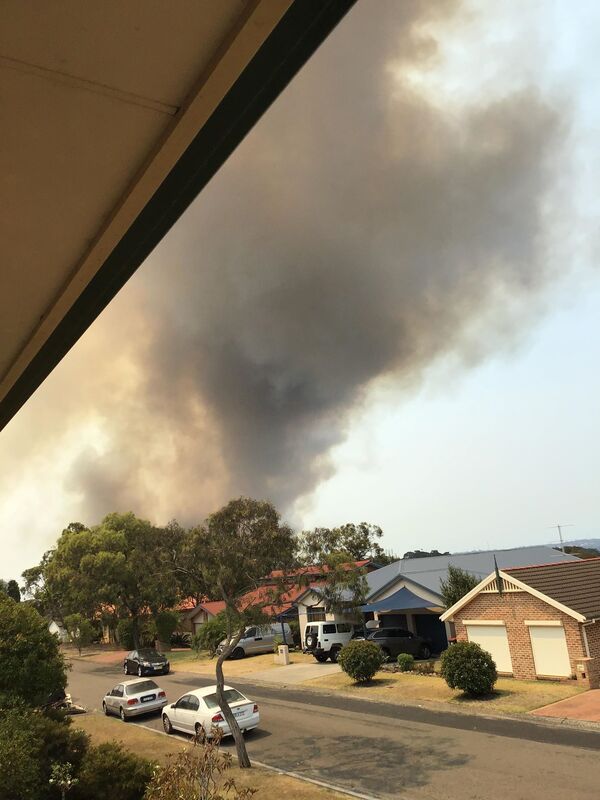
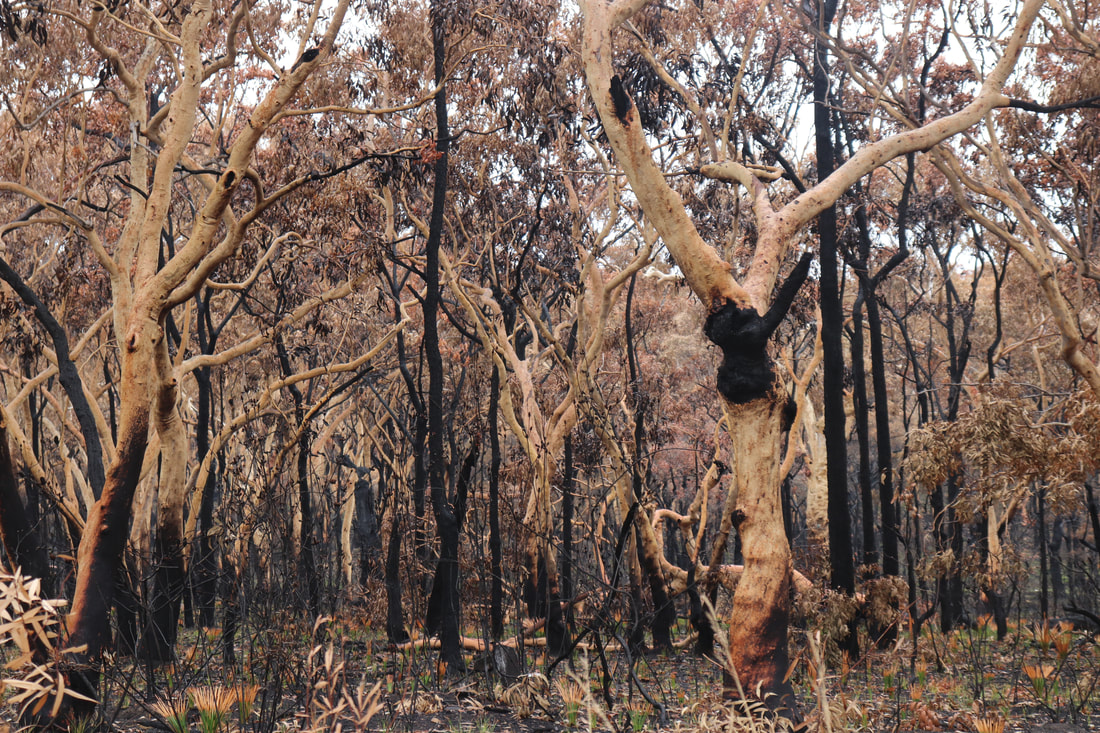
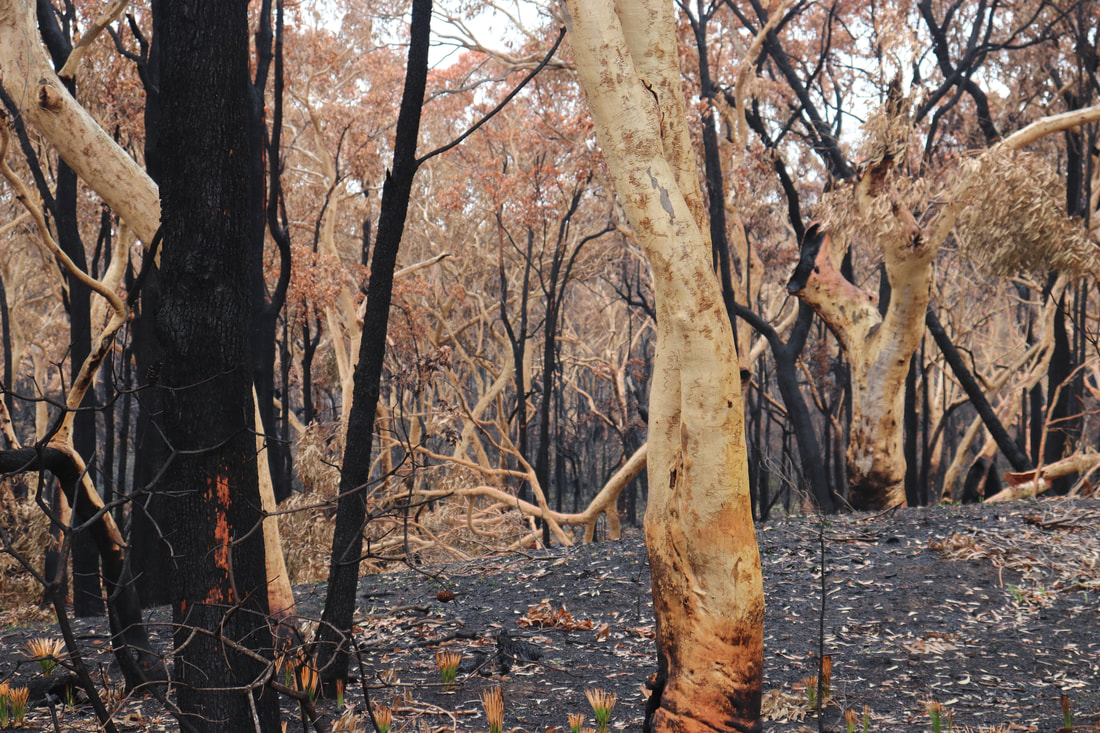
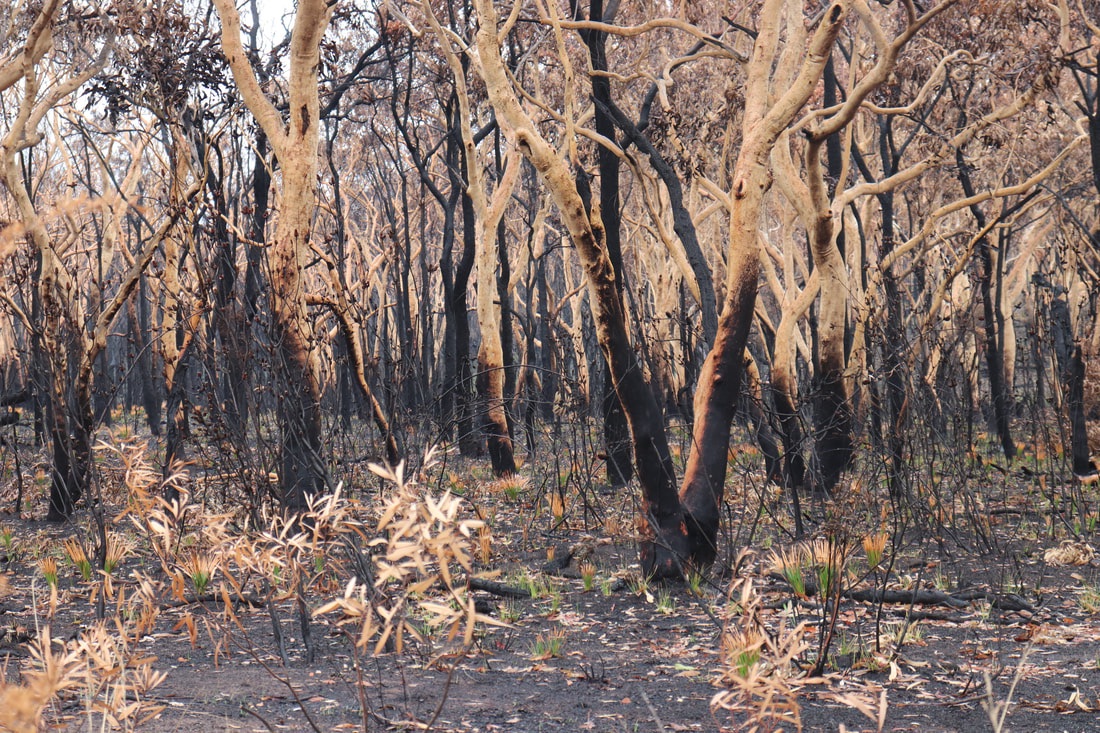
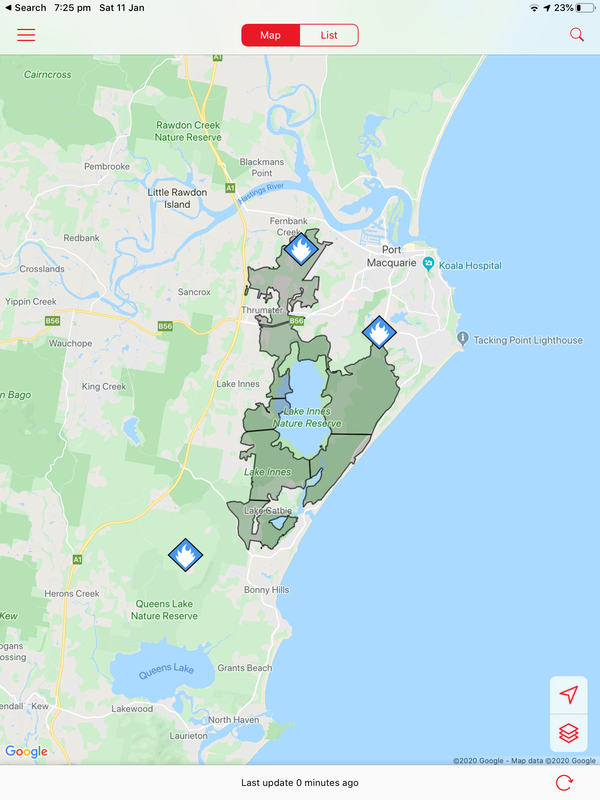
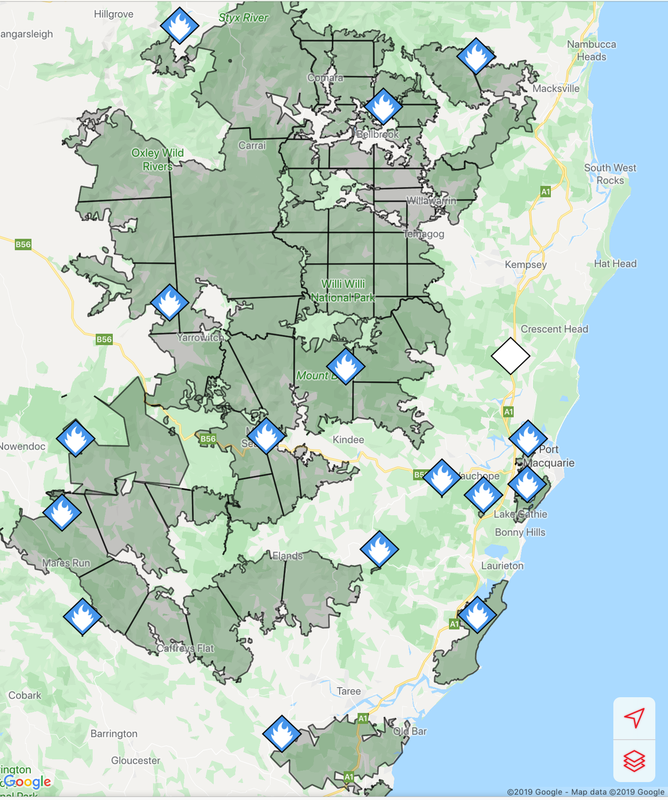
Fires around Port Macquarie, Lake Cathie and Lake Innes began in November 2019. As of 21 January the Crestwood Drive, Port Macquarie fire had burnt out 3572ha, while the connected Lindfield Park rd, Port Macquarie fire had burnt out 859ha.
The Lake Innes Nature Reserve was home to a flourishing koala colony. Between 350 and 600 koalas are believed to have died in the fires around the Lake Innes area. The image on the left is a screenshot of the RFS Fires Near Me app showing the location and extent of the Port Macquarie fires. The screenshot on the right shows the size of the Port Macquarie fires in relation to other fires in the mid-North Coast region.
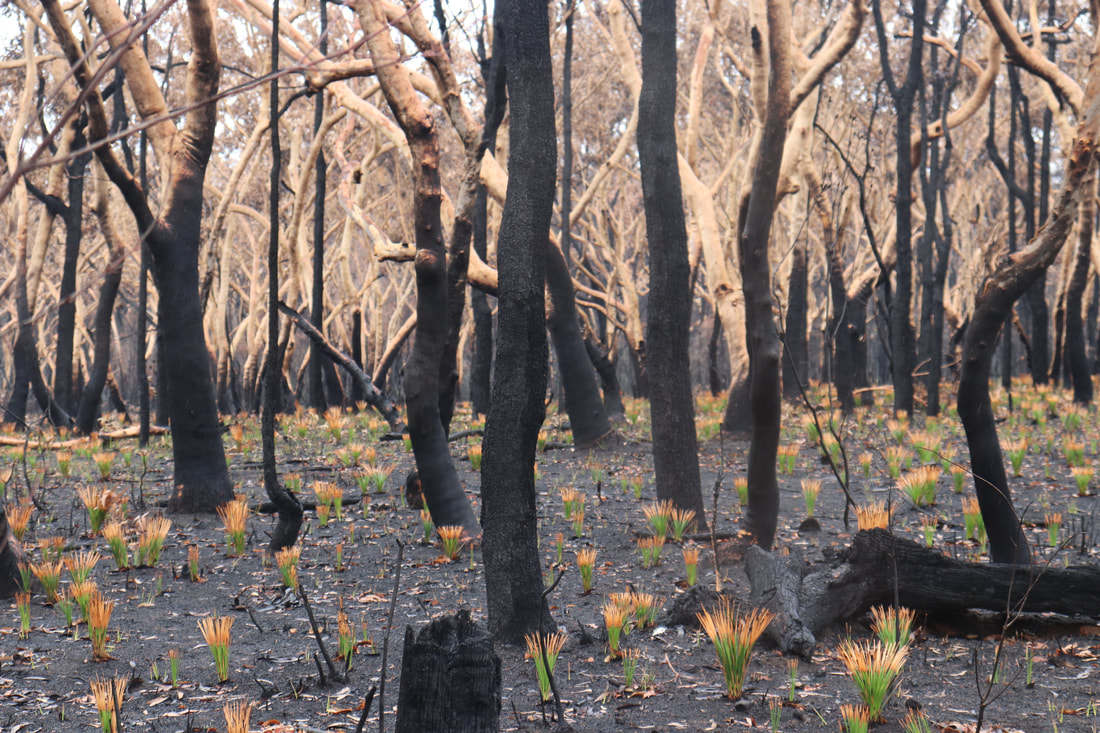
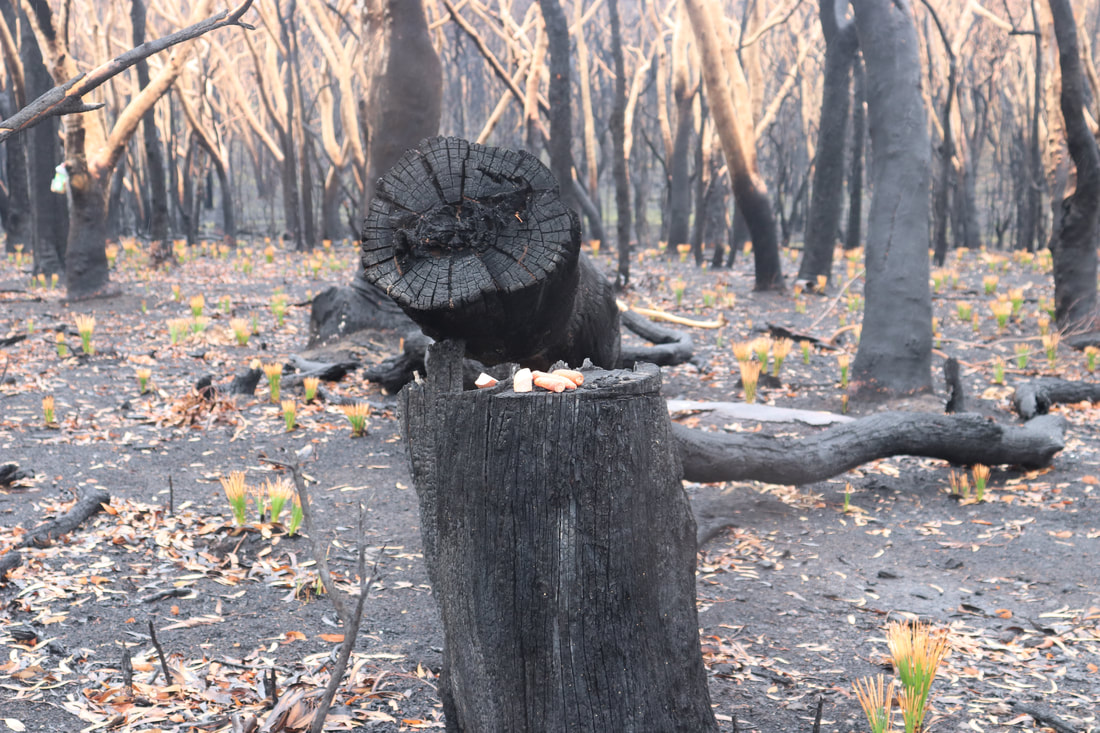
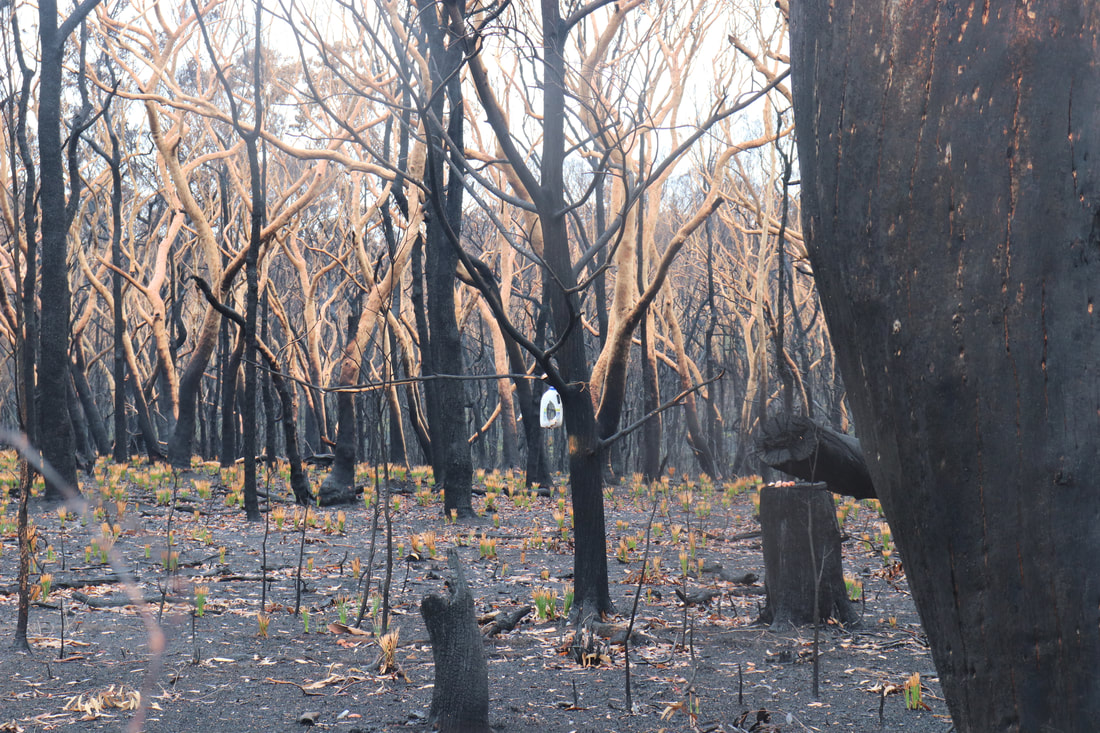
Photos below show the aftermath of the fire - taken on 17 January, 2020.
The post below from NSW National Parks and Wildlife Services indicate that while the fire around Lake Innes was extinguished, there remains risk for future fires flaring even several months later. The post below was posted on January 21.
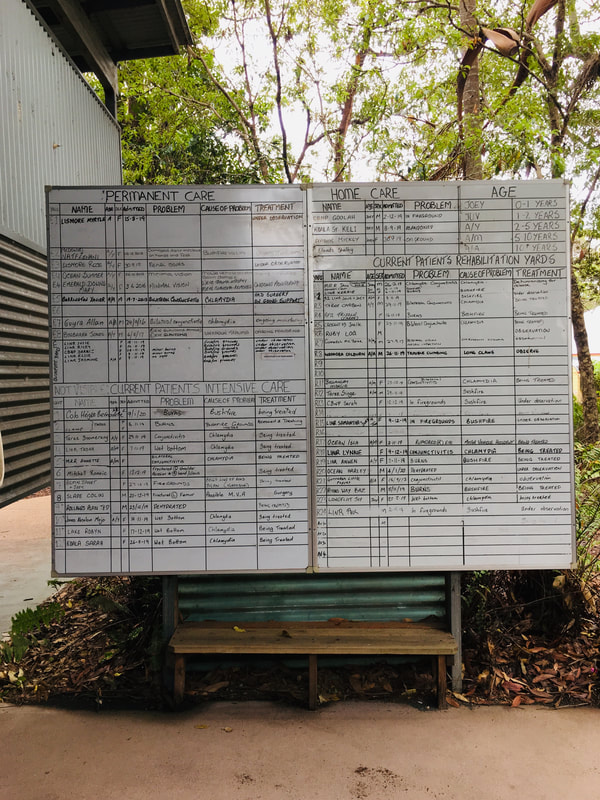
Port Macquarie Koala Hospital
Following the fire a number of injured koalas required intensive care. The Port Macquarie Koala Hospital was inundated
The Port Macquarie Koala Hospital has a large number of koalas in care. The least injured/ill koalas are available for public viewing, while those most injured are screened from public viewing for their own wellbeing. Below is an example of the management of koalas, their injury/illness and treatment.
Go Fund Me Campaign
Port Macquarie Koala Hospital set up a Go Fund Me Page to raise much needed funds to support care for injured koalas and to establish drinking stations and a breeding program for koalas in the region. The initial goal was for $25,000. By 21 January, the campaign had raised nearly $7.5 million dollars. The scope of the projects originally proposed have now been expanded in light of the huge amount of money raised. Port Macquarie Koala Hospital - Go Fund Me.
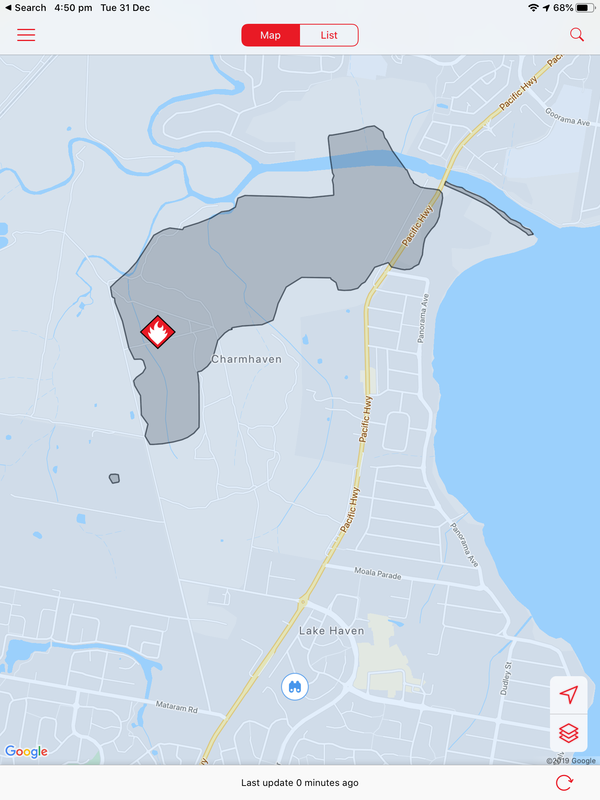
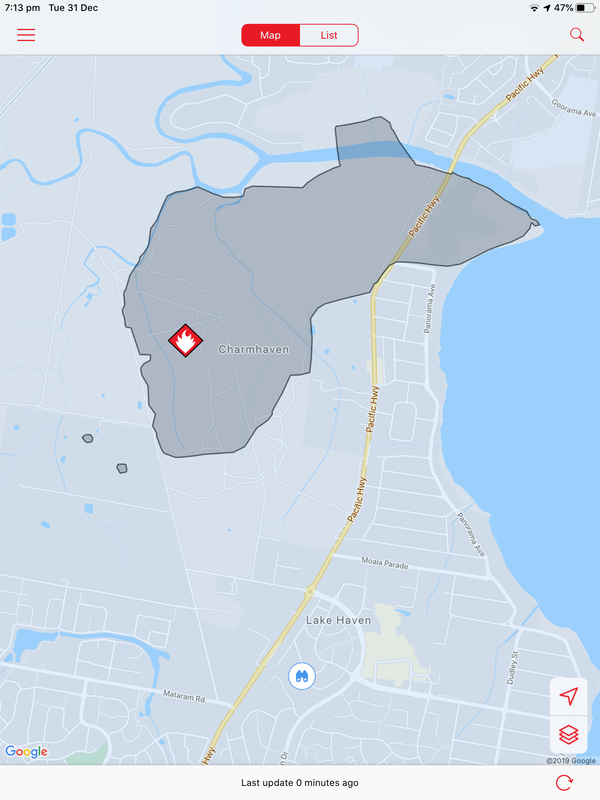
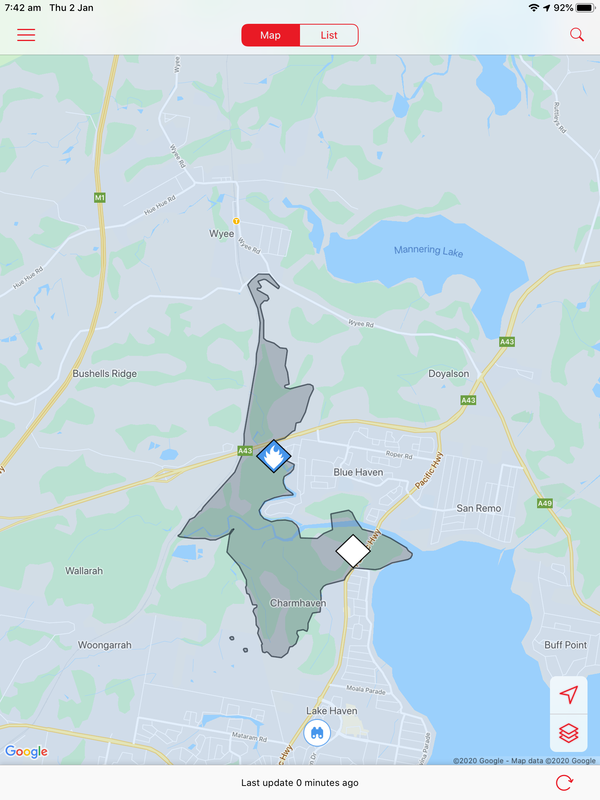
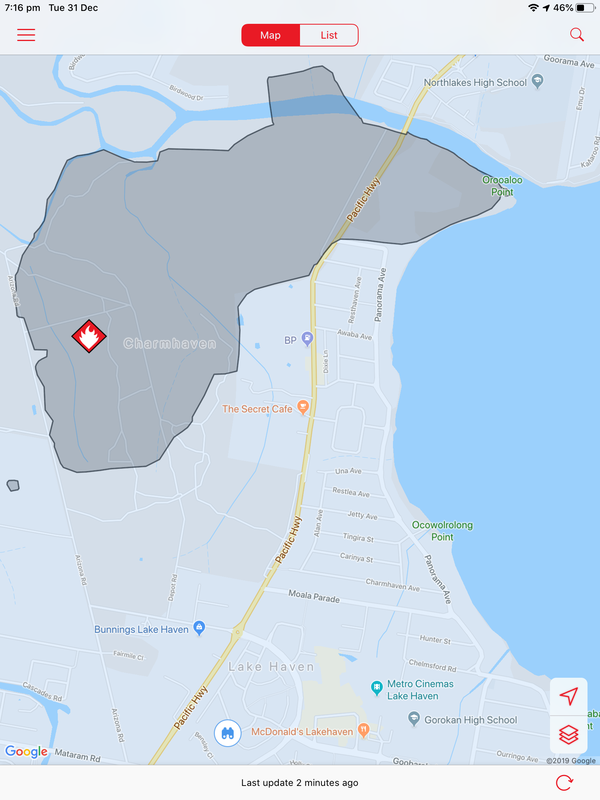
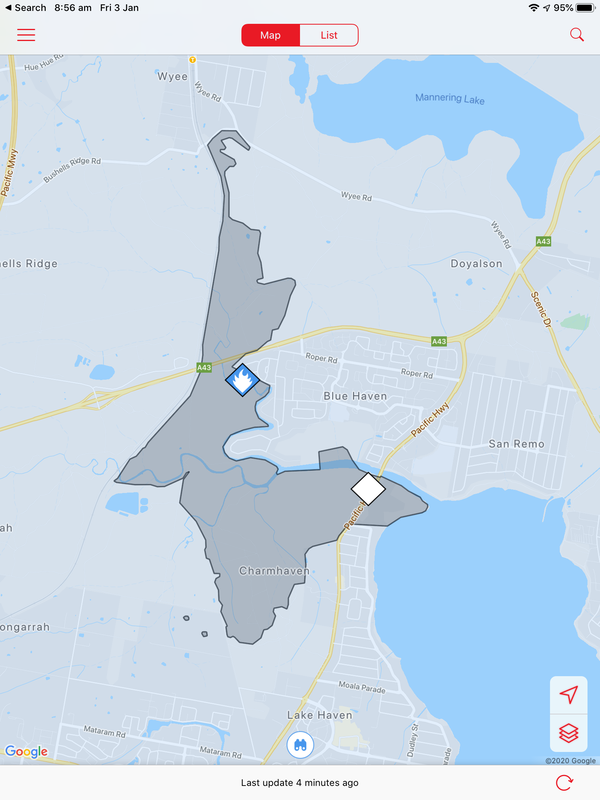
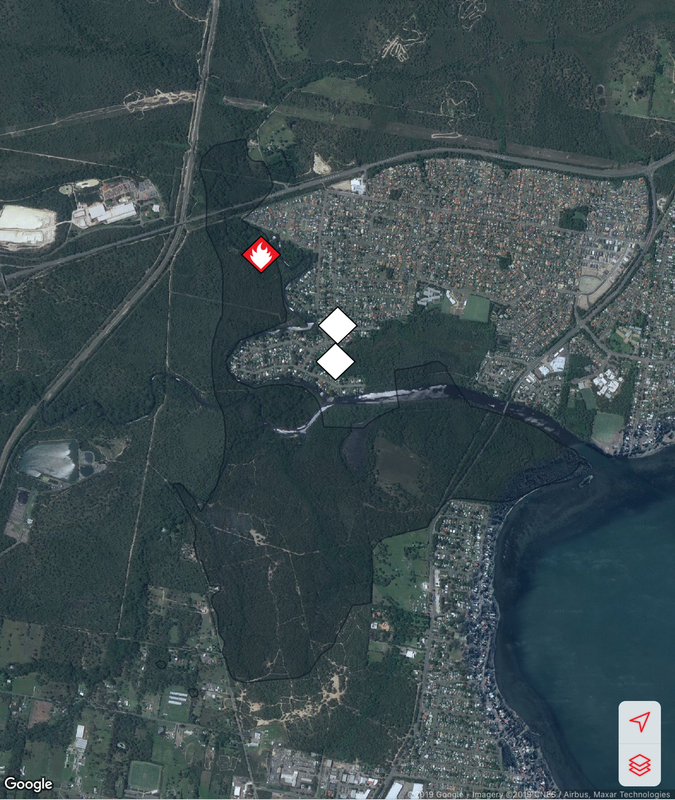
A bushfire started on December 31 at Charmhaven on the Central Coast and burned over several days. This is one of the smaller fires in The Australian Bushfires 2019-2020, but still burnt out 418ha of land. Local residents were issued with warnings and in some cases were evacuated. Two homes, located on Birdwood Drive and Arizona Drive were lost.
The photos below show the aftermath of the fire, taken on 18 January. There is some evidence of regrowth, but the fire-ground still smelt of smoke and was still hot underfoot.
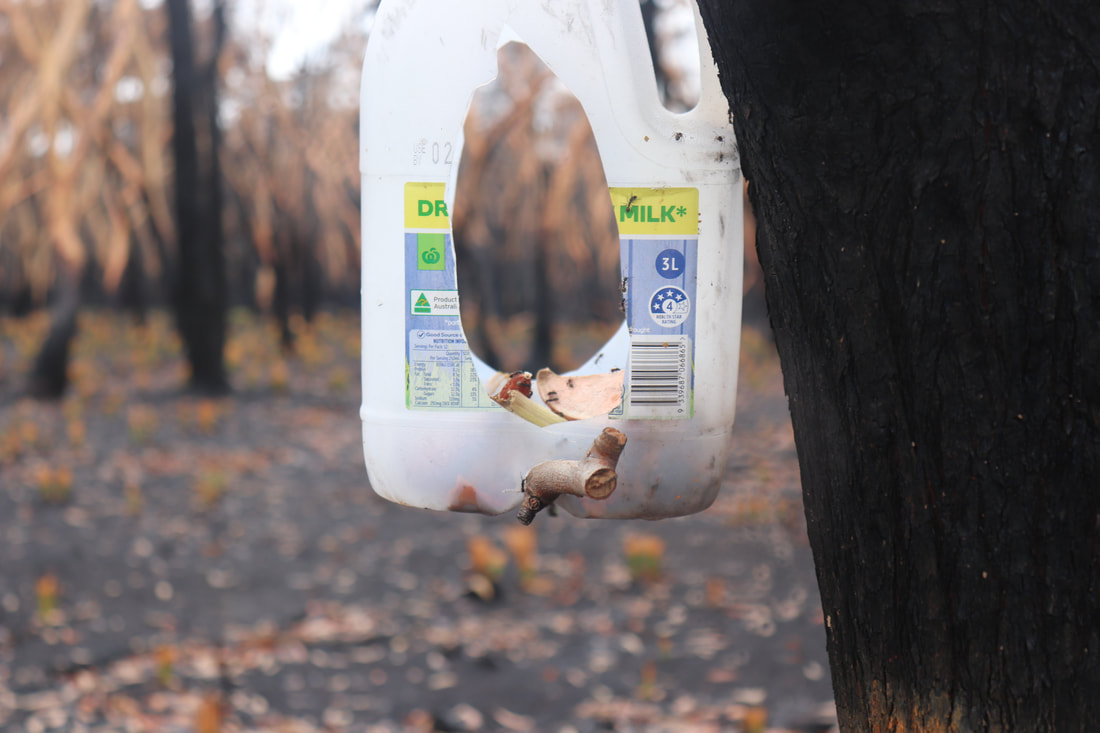
Community groups have attempted to rescue injured wildlife and provide food for them. Below are photos of food left in a hanging container and food left on a tree stump.
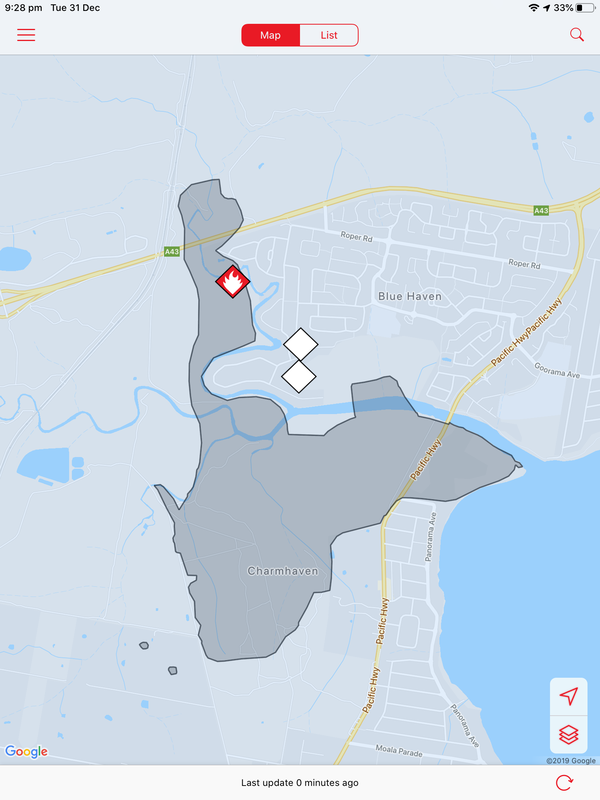
Coordination of feeding and watering stations has been aided by the using of spatial technologies such as Google maps.
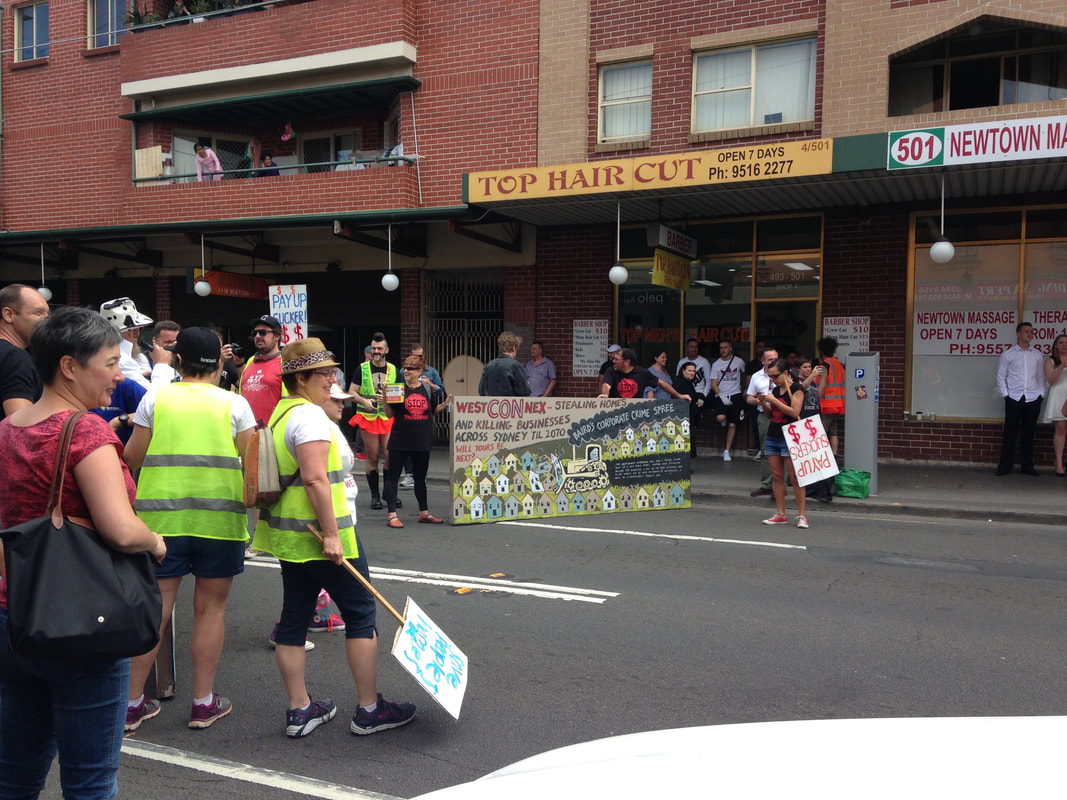
A Water Our Wildlife CCWSAR Map has been developed to help volunteers know where feeding and watering stations have been set up, so that people can visit them independently and re-stock them.. This is part of a unit of work for Changing Places - Australia's Urban Future. Lesson 1: Australia's Projected Population Growth Lesson 2: Implications for Future Growth and Sustainability Lesson 3: Sydenham to Bankstown Urban Renewal Precinct Lesson 4: WestConnex - Sydney, Sustainability and Transport Lesson 4: Sydney Sustainability and Transport (Teacher's Notes) Lesson 5: The GreenWay Lesson 5: Deindustrialisation Lesson 6: Create an infographic Lesson 7: Contributing to a Sustainable Urban Future Lesson 7: WestConnex - Protest Movements and Impacts Lesson 7: Conflict Over Dulwich Hill OR See the complete unit on the Changing Places website. Sydney’s Inner West is still experiencing deindustrialization as industrial land users continue to move further west. Zoning for high density residential developments has exacerbated the increase in land values of industrial properties in Inner West suburbs. As a result some of the last remnants of the suburbs’ blue collar, industrial working class history are being redeveloped. Old waterfront industrial sites such as Rozelle Bay and White Bay have already been rezoned as part of the Bays Precinct urban renewal initiative. Recent rezoning for high density residential housing in suburbs such as Marrickville and Dulwich Hill will see a decline in small industries in coming years. Fieldwork: Visit Marrickville, and take photographs that show evidence of change occurring. Examine the main street, Marrickville rd. Conduct an environmental survey on the main street. Conduct a landuse survey of Marrickville. Use an outline map of the suburb, and shade in different colours to represent different landuses (yellow – low density residential, brown – high density residential, red – commercial, grey - industrial, blue – public facilities/institutions, green – recreation). Compare your landuse survey to the proposed plans for Marrickville and describe the landuse changes that will take place. Lesson Activity: Deindustrialisation Choose one suburb that will be changed by the Planned Precincts. Create a digital map that shows the existing density of the suburb, and another map which shows the proposed density of the suburb. Use Google Maps to help you create your map. Use flowcharts and mind maps to visually represent the changes that are occurring in Sydney’s Inner West. You may choose to group your ideas around specific suburbs or developments.
This is part of a unit of work for Changing Places - Australia's Urban Future. Lesson 1: Australia's Projected Population Growth Lesson 2: Implications for Future Growth and Sustainability Lesson 3: Sydenham to Bankstown Urban Renewal Precinct Lesson 4: WestConnex - Sydney, Sustainability and Transport Lesson 4: Sydney Sustainability and Transport (Teacher's Notes) Lesson 5: The GreenWay Lesson 5: Deindustrialisation Lesson 6: Create an infographic Lesson 7: Contributing to a Sustainable Urban Future Lesson 7: WestConnex - Protest Movements and Impacts Lesson 7: Conflict Over Dulwich Hill OR See the complete unit on the Changing Places website. Community groups lobbied for the continuation of a Greenway Trail along the light rail corridor to link up with the Cooks River cycleway. The Cooks River to Iron Cove GreenWay is a green corridor following the route of the Rozelle to Dulwich Hill light rail line. It is shared pedestrian and cyleway that links the Cooks River Cycleway and the Iron Cove BayRun. The combination of both light rail and the Greenway encourages public transport use and cycling/walking both for recreation and commuting, reducing some of the car dependence in this part of Sydney. In addition to providing opportunities for residents to choose cycling and walking as an alternative to car travel, it also provides a habitat corridor, linking several bushcare sites in the Inner West. Fieldwork: Visit a site along the GreenWay. Walk along the greenway and choose 3 separate locations to complete an environmental survey. Compare the results of the 3 surveys. Explain how the Greenway contributes to the sustainability of the Inner West. This is part of a unit of work for Changing Places - Australia's Urban Future. Lesson 1: Australia's Projected Population Growth Lesson 2: Implications for Future Growth and Sustainability Lesson 3: Sydenham to Bankstown Urban Renewal Precinct Lesson 4: WestConnex - Sydney, Sustainability and Transport Lesson 4: Sydney Sustainability and Transport (Teacher's Notes) Lesson 5: The GreenWay Lesson 5: Deindustrialisation Lesson 6: Create an infographic Lesson 7: Contributing to a Sustainable Urban Future Lesson 7: WestConnex - Protest Movements and Impacts Lesson 7: Conflict Over Dulwich Hill OR See the complete unit on the Changing Places website. Social Movements Social movements can provide residents of a community with a means of influencing their local environment. They provide a way for residents to communicate opinions on planning and other matters to the formal planning structures and organisations, and to intervene in the formal political system. Activities of social movements can include letter-writing campaigns, protest meetings, and media campaigns. Social movements can be important agents of urban change and can empower local communities. An example of a social movement is the urban cycling movement which aims to reduce car dependence and improve sustainability of transport, increase safety on roads for cyclists and encourage a collective increase in personal health and wellbeing through exercise. Resident Action Groups Resident Action Groups are a form of social movement at a smaller scale, and usually involve issues of a short term nature. RAGs often tend to be localized and single-focused. Although these groups are usually designed to force significant changes in society as a whole, they can at times bring about change at a smaller scale. Unlike social movements more generally, RAGs are more obviously limited and can be interpreted as having NIMBY (not in my backyard) motives. Recent transport infrastructure development and proposals for high density throughout the Inner West of Sydney have created an increase in the number of RAGs and concentrated the patterns of RAGs around development sites. There are currently a large number of Resident Action Groups in the Inner West of Sydney protesting and lobbying against WestConnex and increased development. Examples include Rozelle Against WestConnex, Save Dully, and Newtown WestConnex Action Group. Rozelle Against WestConnex The Rozelle Against WestConnex group lobbies against WestConnex in general, but more specifically the Rozelle Interchange in the vicinity of the Rozelle Goods Yard, as well as the tunnels running below Denison and Darling Streets. This will involve acquisition and demolition of homes and businesses and creation of 12-metre high, unfiltered smoke stacks. Save Dully The Save Dulwich Hill Community Group promotes issues related to the redevelopment of the suburbs and lobbies the government to preserve the heritage of suburb. Visit the Save Dully website to read more about their actions. Dulwich Hill experienced growth in the late 1800s following the introduction of the tram line, and as a result contains buildings with heritage architecture, particularly Federation architecture. The Sydenham to Bankstown Urban Renewal Strategy, encompasses the suburb of Dulwich Hill, rezoning for higher density and redevelopment of older buildings. Save Dully is lobbying to ensure that the historic and diverse nature of Dulwich Hill is preserved. Newtown WestConnex Action Group The M4-M5 link tunnels will run underneath Newtown. Many Newtown business owners have begun protesting the development, worried that congestion and bottlenecks will negatively impact retail businesses, or alternatively that clearways along King St will kill business. The Newtown WestConnex Action Group has been formed. In Alexandria a new bridge is being constructed over the canal to allow movement of traffic from the St Peters interchange. Lesson Idea: Individual and community action Examine the ways that individuals and communities have contributed to the political process and discussions about the WestConnex project. Write a paragraph about 5 actions taken by individuals and communities. Do you think these have been effective? Do you think these actions are justified? What other actions could individuals or communities take? Examine a video of a council meeting about West Connex (try a simple search on Youtube). Consider how the different groups and individuals perceive how WestConnex impacts their community and/or environment. Choose a persona from one of the following: local resident, local councilor, construction worker, urban planner. Write a series of tweets that you might compose to tell your feelings and opinions about the issue. Take photographs of a site that will be or has been affected by WestConnex. You may use Google Street View if you are not close by to a relevant site. Annotate the photographs showing how features of the environment have changed or will change as a result of the WestConnex development. Assess how the changes to the site will impact on its environmental quality. Obtain aerial photographs of the Inner West of Sydney (these may be screen shots from Google Maps). Visually represent the changes that are taking place in the area. Annotate the aerial photographs showing locations affected by Planned Precincts, WestConnex and the Metroline. Include detail about the types of changes that are going to take place. Fieldwork: Questionnaire
Conduct a questionnaire on residents that live in the Inner West of Sydney. Design 8-10 questions to ask. Some examples:
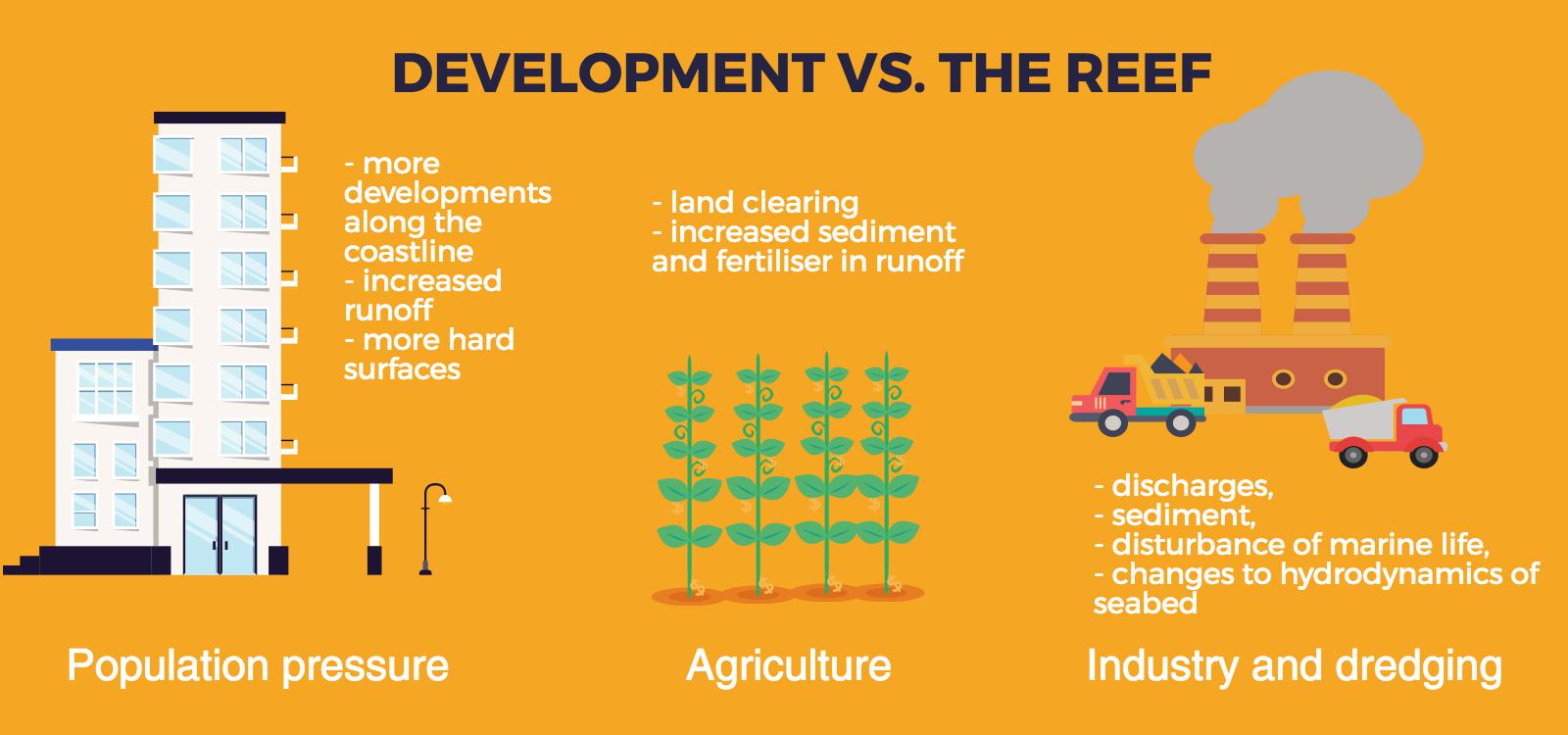
There is a huge amount of information available about coral reef health and in particular the mass coral bleaching events that have occurred over the past two years. Two of my previous posts are linked below, but if you scroll to the bottom of the page there are a range of other articles, reports and websites regarding coral bleaching that you might find useful.
Previous posts: Mass coral bleaching events Coral bleaching - reef resilience Students should define the following key terms: - acclimatise - connectivity - recruit - adaptation - natural selection - symbiotic - zoozanthallae - parasite - photosynthesis Answer the questions below. Conduct internet research to find articles and reports which support your answers.
Resources: Coral bleaching - GBRMPA Coral bleaching and the Great Barrier Reef - ARC CoE Coral bleaching: Extreme heat pushes parts of the Great Barrier Reef beyond recovery - ABC Coral bleaching events - AIMS Great Barrier Reef: a "hopping hotspot" - Australian Geographic |
Categories
All
Archives
May 2024
|
||||||||||||||||