Gradient
Gradient is a measure of the steepness of a slope between two points.
Gradient = rise over run OR rise
run
If the difference in height between the two points is 40 m, and the distance between the two points is 4 km the gradient would be:
40m 4 1
4000m 400 100
This means that for every 100m distance (run) there is a rise of 1 metre.
Gradient = rise over run OR rise
run
If the difference in height between the two points is 40 m, and the distance between the two points is 4 km the gradient would be:
40m 4 1
4000m 400 100
This means that for every 100m distance (run) there is a rise of 1 metre.
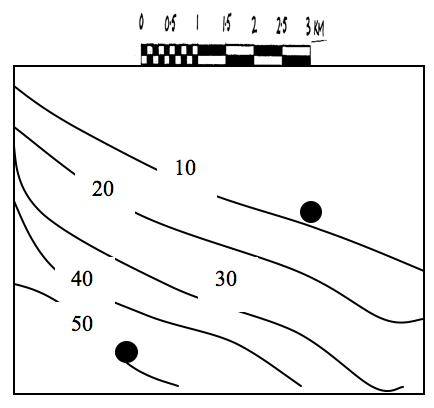
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 210 metres, Point B has a height of 70 metres, the distance between the
two points is 14cm, and the scale of the map is 1:100,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 180 metres, Point B has a height of 150 metres, the distance between the two points is 15cm, and the scale of the map is 1:100,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 150 metres, Point B has a height of 100 metres, the distance between the
two points is 10cm, and the scale of the map is 1:100,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 80 metres, Point B has a height of 70 metres, the distance between the
two points is 4cm, and the scale of the map is 1:100,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 500 metres, Point B has a height of 400 metres, the distance between the two points is 6cm, and the scale of the map is 1:50,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 1000 metres, Point B has a height of 750 metres, the distance between the two points is 20cm, and the scale of the map is 1: 50,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 640 metres, Point B has a height of 590 metres, the distance between the two points is 15cm, and the scale of the map is 1:50,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 50 metres, Point B has a height of 25 metres, the distance between the
two points is 4cm, and the scale of the map is 1:50,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 90 metres, Point B has a height of 50 metres, the distance between the
two points is 8cm, and the scale of the map is 1:100,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 1000 metres, Point B has a height of 500 metres, the distance between the two points is 12cm, and the scale of the map is 1:50,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 90 metres, Point B has a height of 80 metres, the distance between the
two points is 8cm, and the scale of the map is 1:50,000.
two points is 14cm, and the scale of the map is 1:100,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 180 metres, Point B has a height of 150 metres, the distance between the two points is 15cm, and the scale of the map is 1:100,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 150 metres, Point B has a height of 100 metres, the distance between the
two points is 10cm, and the scale of the map is 1:100,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 80 metres, Point B has a height of 70 metres, the distance between the
two points is 4cm, and the scale of the map is 1:100,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 500 metres, Point B has a height of 400 metres, the distance between the two points is 6cm, and the scale of the map is 1:50,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 1000 metres, Point B has a height of 750 metres, the distance between the two points is 20cm, and the scale of the map is 1: 50,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 640 metres, Point B has a height of 590 metres, the distance between the two points is 15cm, and the scale of the map is 1:50,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 50 metres, Point B has a height of 25 metres, the distance between the
two points is 4cm, and the scale of the map is 1:50,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 90 metres, Point B has a height of 50 metres, the distance between the
two points is 8cm, and the scale of the map is 1:100,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 1000 metres, Point B has a height of 500 metres, the distance between the two points is 12cm, and the scale of the map is 1:50,000.
Work out the gradient of the slope if Point A has a height of 90 metres, Point B has a height of 80 metres, the distance between the
two points is 8cm, and the scale of the map is 1:50,000.