Topographic map basics
Topographic map basics include:
- area and grid references
- contour lines
- local relief
- distance, time and speed travel
- aspect
- altitude
- river flow
- quadrants
- directions
- bearings
- scale
Elements of a Map
B - Border
O - Orientation
L - Legend
T - Title
S - Scale
O - Orientation
L - Legend
T - Title
S - Scale
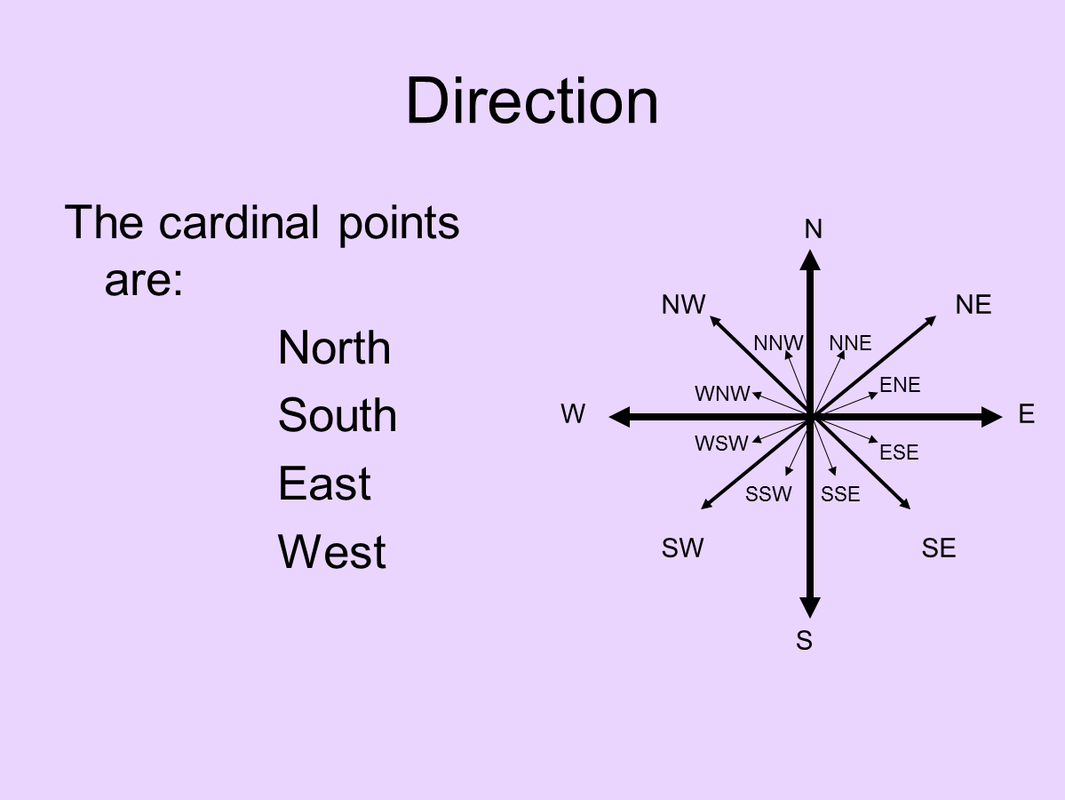
Direction
Scale
1:100,000 means that 1cm on the map is equivalent to:
- 1000m
- 1km
1:250,000 means that 1cm on the map is equivalent to:
- 2,500m
- 2.5km
1:50,000 means that 1cm on the map is equivalent to:
- 500m
- 1/2 km
1:25,000 means that 1cm on the map is equivalent to:
- 250m
- 1/4 km
Large scale are used to show detail, e.g. a street directory.
Small scale are used to show detail, e.g. a satellite image of NSW.
Oblique maps and photos have scales that vary from one part of the image to another (remember that an oblique photograph is taken at an angle).
- 1000m
- 1km
1:250,000 means that 1cm on the map is equivalent to:
- 2,500m
- 2.5km
1:50,000 means that 1cm on the map is equivalent to:
- 500m
- 1/2 km
1:25,000 means that 1cm on the map is equivalent to:
- 250m
- 1/4 km
Large scale are used to show detail, e.g. a street directory.
Small scale are used to show detail, e.g. a satellite image of NSW.
Oblique maps and photos have scales that vary from one part of the image to another (remember that an oblique photograph is taken at an angle).
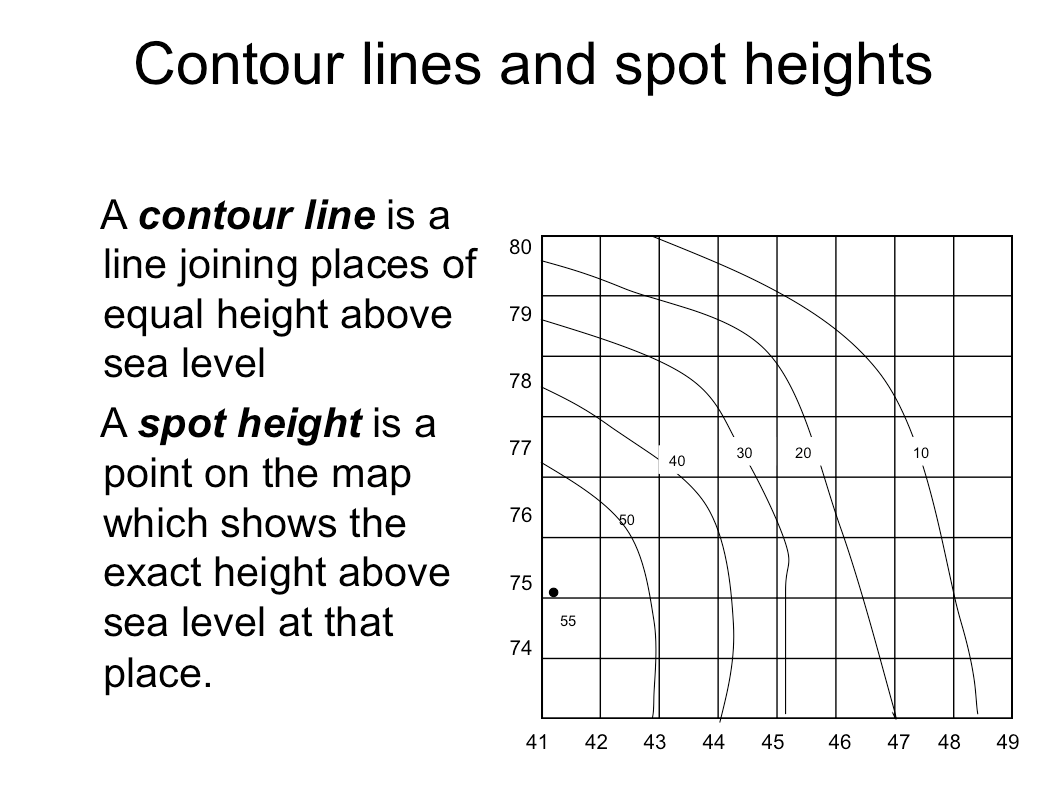
Contour lines
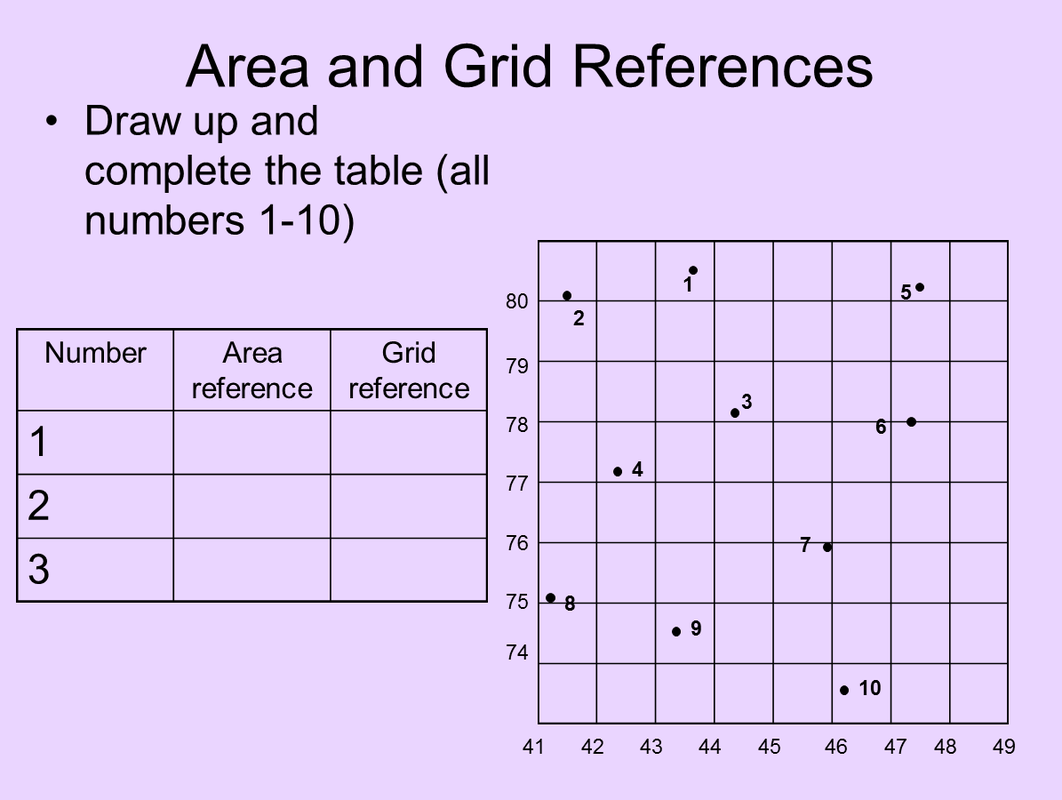
Area and Grid Reference
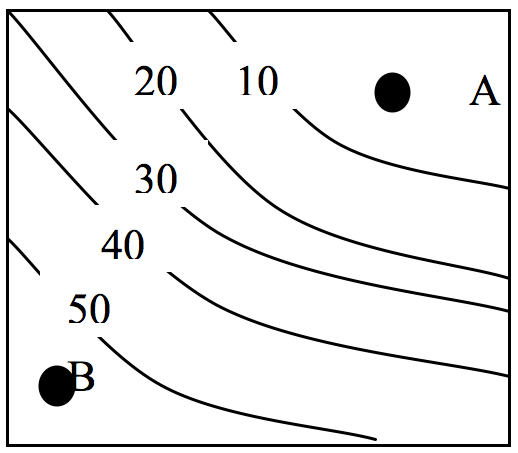
Local Relief
Local Relief is the difference in height between two locations.
Local relief = the highest point – the lowest point
Example:
Point A would have a height of approximately 5m.
Point B would have a height of approximately 55 m
So the highest point minus the lowest point would be:
55m-5m = 50m
Local relief = 50m
Local relief = the highest point – the lowest point
Example:
Point A would have a height of approximately 5m.
Point B would have a height of approximately 55 m
So the highest point minus the lowest point would be:
55m-5m = 50m
Local relief = 50m
Work out the local relief if Point has a height of 734 and Point B has a height of 533.
Work out the local relief if Point has a height of 964 and Point B has a height of 234.
Work out the local relief if Point has a height of 874 and Point B has a height of 532.
Work out the local relief if Point has a height of 945 and Point B has a height of 423.
Work out the local relief if Point has a height of 644 and Point B has a height of 254.
Work out the local relief if Point has a height of 744 and Point B has a height of 85.
Work out the local relief if Point has a height of 964 and Point B has a height of 234.
Work out the local relief if Point has a height of 874 and Point B has a height of 532.
Work out the local relief if Point has a height of 945 and Point B has a height of 423.
Work out the local relief if Point has a height of 644 and Point B has a height of 254.
Work out the local relief if Point has a height of 744 and Point B has a height of 85.
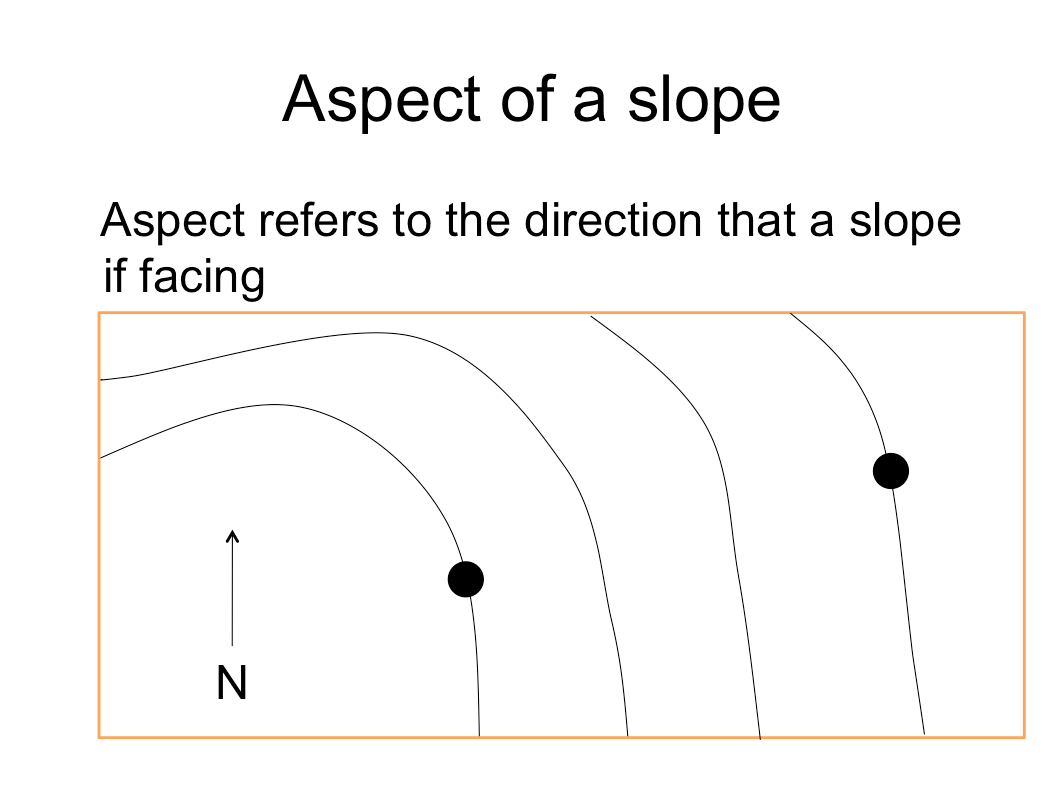
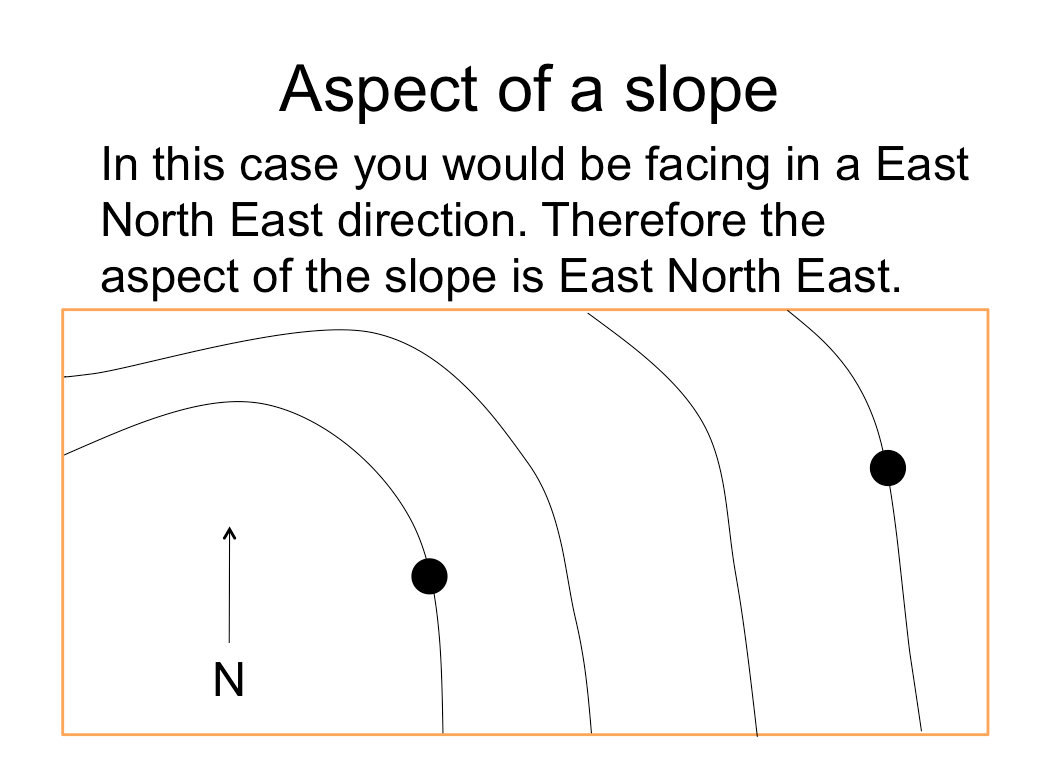
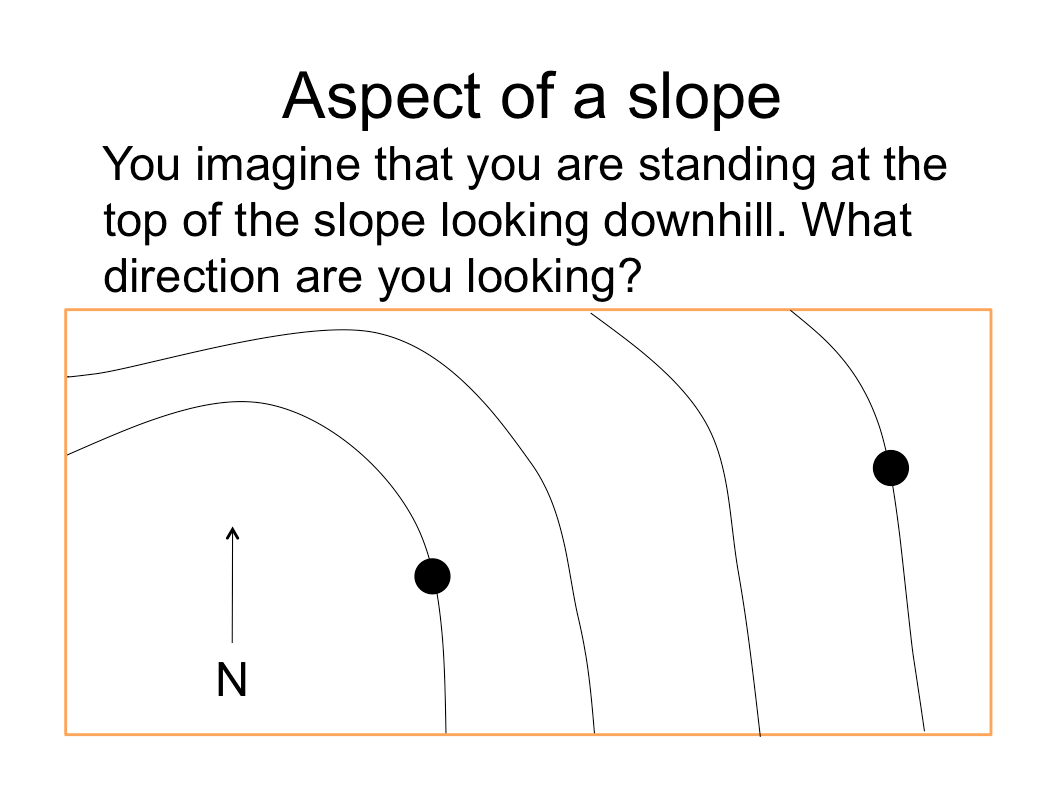
Aspect
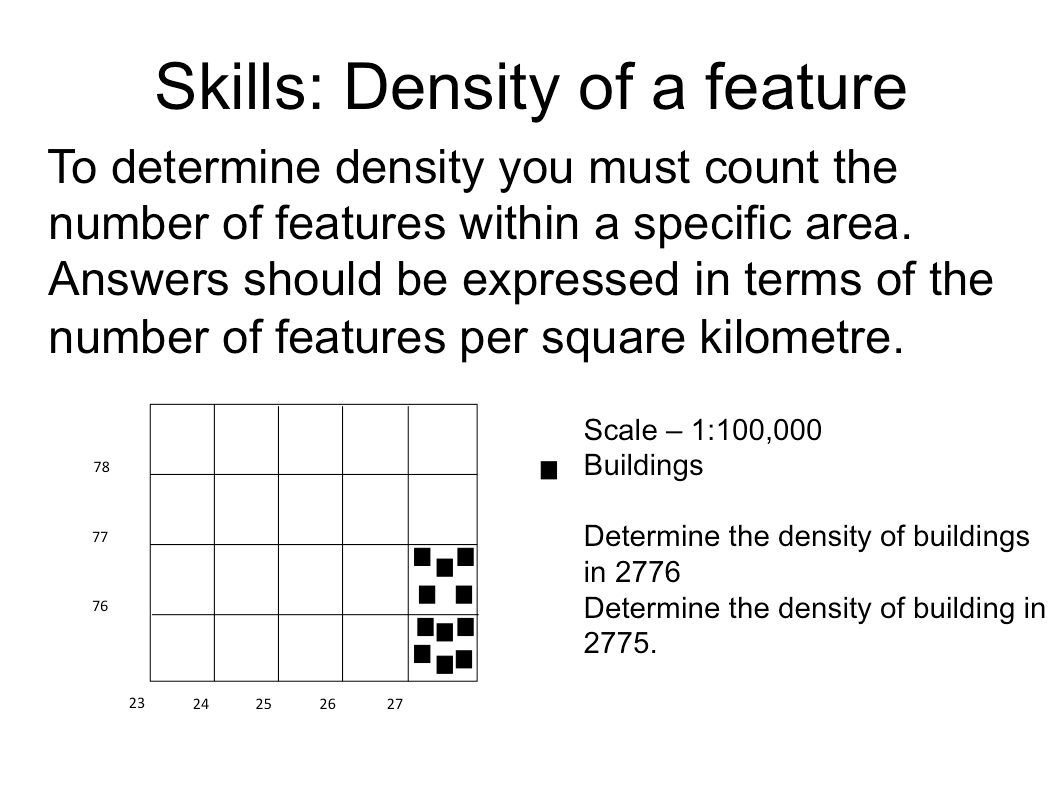
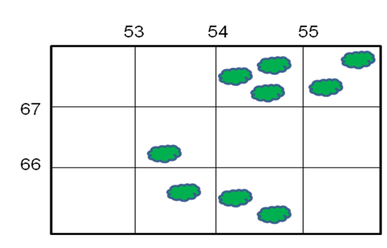
Density
|
Density refers to the number of times a particular feature is found in a particular area. For example, the number of trees in a square kilometre.
Examine the diagram below. Assume that each square is 1km2. 1. What is the density of trees in: a. 5367 ................... b. 5466 ................... c. 5567 ................... d. 5465 ................... e. 5366 ................... 2. What is the average density of trees on the entire map. (You will need to count all the trees, work out how many km2 are on the map, and divide the number of trees by the number of km2). ................... |