Population Pyramids
|
Key terms:
Population structure Dependency ratio Population pyramids show the age and gender structure of a population. They can be used to predict what will happen in the future and predict what services may be needed. · Population pyramids are an important tool used in demography. · Age distribution of the population can be seen at a glance. A country with a broad, wide base: · has a very high birth rate · has very young population · needs schools, baby health centres, support for families and mothers A country with large groups of older people: · needs retirement homes · recreational activities for older people · money to pay old age pensions or alternate polcies to address the social and economic needs of the elderly. The dependency ratio of a population refers to the percentage of the population which is over 65 together with those under 15. Together, this part of the population is considered to be out of the work force and therefore they must be supported by the rest of the population. |
|
|
How to draw a population pyramid:
|
|
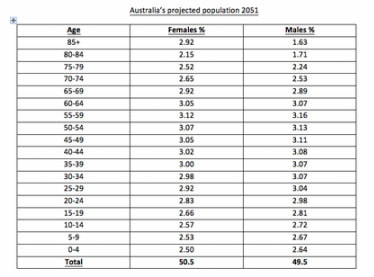
Task: Using the data from the table below: (Use grid paper)
(i) Graph the data on a population pyramid; use a RED pen to graph the data for males and a BLUE pen to graph the data for females. (ii) Which age group is likely to be the largest in 2051? (iii) What facilities will they need? (iv) What implications do you think the data would have for the nature of Australian society? (v) Which age group will you belong to? How do you think you will be contributing to society? Note: Select an appropriate scale for your graph! Consider whether the data is on percentage (%) or real figures(e.g. ‘000s) |
Accessing global population pyramids
Populationpyramids.net allows you to examine population pyramids of countries from 1950 to present, and predictions into 2100. Examine Populationpyramids...
Populationpyramids.net allows you to examine population pyramids of countries from 1950 to present, and predictions into 2100. Examine Populationpyramids...