Population movements
Stage 6 content:
Population and resource consumption
- influences that shape global population change, including:
- demographic transition
- population movements
Population and resource consumption
- influences that shape global population change, including:
- demographic transition
- population movements
Population Movements
Key terms:
migration
immigration
emigration
refugee
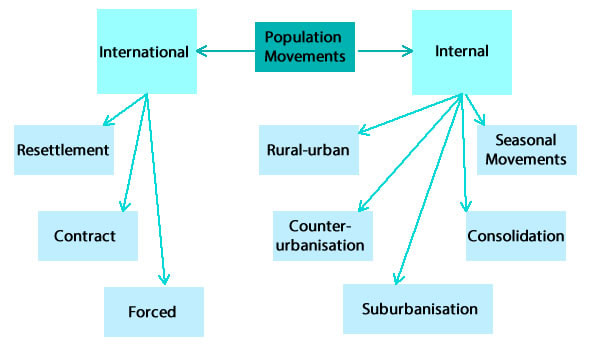
There are two main types of population movements – International (between countries) and Internal (within a country).
International Population Movements
Many contemporary migrations are closely related to the economic, political and cultural links being formed between nations due to the process of globalisation.
Types of international migration are:
- Resettlement migration
- Contract migration - guest workers, business migration, student migrant
- Forced migrations – the “slave trade”, refugees
Internal Population Movements
Types of internal migration are:
- Rural-Urban migration
- Counter-urbanisation
- Population movements to regions where the growth of the service sector is greatest (a developed world phenomenon)
- Suburbanisation
- Urban consolidation/ gentrification (a developed world phenomenon)
- Seasonal movements
Key terms:
migration
immigration
emigration
refugee
There are two main types of population movements – International (between countries) and Internal (within a country).
International Population Movements
Many contemporary migrations are closely related to the economic, political and cultural links being formed between nations due to the process of globalisation.
Types of international migration are:
- Resettlement migration
- Contract migration - guest workers, business migration, student migrant
- Forced migrations – the “slave trade”, refugees
Internal Population Movements
Types of internal migration are:
- Rural-Urban migration
- Counter-urbanisation
- Population movements to regions where the growth of the service sector is greatest (a developed world phenomenon)
- Suburbanisation
- Urban consolidation/ gentrification (a developed world phenomenon)
- Seasonal movements
Population movement occurs for a number of reasons:
- Territorial expansion
- People wanting better living conditions or education
- Employment
- To join relatives and friends
- Natural disasters
- Wars and conflicts
- Enslavement
- Religious and political persecution
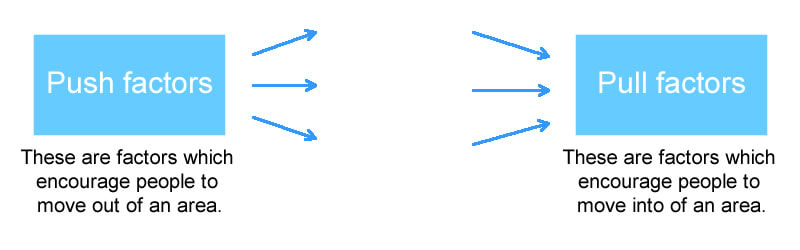
Push and Pull factors
There are a range of factors which push people away from areas and other factors which pull people to particular places. Push factors include poverty, political persecution, starvation, war, unemployment. Pull factors include family reunion, employment, better services and political freedom.
- Territorial expansion
- People wanting better living conditions or education
- Employment
- To join relatives and friends
- Natural disasters
- Wars and conflicts
- Enslavement
- Religious and political persecution
Push and Pull factors
There are a range of factors which push people away from areas and other factors which pull people to particular places. Push factors include poverty, political persecution, starvation, war, unemployment. Pull factors include family reunion, employment, better services and political freedom.
Push factors encourage people to move away from an area. These could include economic hardships such as poverty, high levels of debt, unemployment and the inability to access resources. In some cases political issues can encourage people to leave an area such as war or conflict or political persecution. Overpopulation of an area can add pressure on existing services and supplies and result in food shortages and starvation or malnourishment. Disasters can force people out of an area by rendering it unliveable.
Pull factors attract people to a particular area. Some people move into an area to join family and friends who moved there earlier. People who have suffered through political conflicts can be attracted to areas that are politically stable and where political freedom and freedom of expression are valued. People are attracted to areas by the promise of better services and facilities, opportunities like education and employment and higher incomes.