|
Linking to other websites
You can provide a link to another website without attribution as the website will have its own logos, copyright information, etc. associated. However, if a website has a document available that you download, you can’t legally upload the document onto your site. You can only link to the document in its existing location. For example you can’t download a HSC exam of syllabus document and upload it onto your site. Youtube and Google Maps Some website creators/blogs allow you to directly embed Youtube clips and Google Maps onto your webpage. When you do this, you are actually providing a link to the Youtube site or Google site and as a result you don’t need to attribute/cite the source. The Youtube or Google logos will show on your website where you have embedded the resource. Youtube has the responsibility to ensure that their users meet copyright regulations. For example if there is a clip of the Sydney Symphony Orchestra playing a piece by Beethoven, it is the responsibility of Youtube to address the copyright issues. If you decided to take a screen shot from a Youtube clip or Google Maps application this would require attribution. Music Music is very difficult to work with in online publishing. Copyright applies to both the performance of music and the written piece of music. In most cases a licence must be paid for use of music online which can be very expensive. A work-around is to embed a Youtube clip of the music being performed to pass on the copyright responsibilities to a third party. Using material from other websites If you want to use material from other websites it is best to just link to the site. However in the case where you just have a small section of text it is fine to just quote the source and provide a link back to the webpage that you found it. In the case of the Board of Studies, they are very touchy about their property being reproduced. If you use a section of the syllabus for example, type NSW Board of Studies beneath the quote and then link from the words “NSW Board of Studies” to the page the information is found. Working with graphics When creating your class website, you need to be very wary that all the images and graphics that you use are copyright clear and don’t breach any privacy policies of the Department of Education. 1. Use photographs that you have taken yourself. Dig out your holiday snaps. Ideally you don’t want to be using photos of yourself, but you can always edit yourself out if necessary. Don’t forget that most phones these days have pretty good camera capabilities. If you are out somewhere and see a great shot that would work well on your website then take it. 2. Don’t publish photos of students. Most students at the school have signed a “Permission to Publish” form, but some have not. This could be for a whole range of reasons such as a witness protection, domestic violence issues, etc. To avoid any problems it is best to avoid photos with students. If you want to use photos of students doing something or making something try to frame the photo so that you just see the student’s hands or the back of their head. Obviously photos of students are posted on the official school websites, but these go through a series of checks to ensure that no-one is published that shouldn’t be. 3. Use image repositories. Sites such as wikicommons, flickr, shutterstock, and getty images allow some of their images to be used in online projects without citing the source (some of these will also require that you pay for them). Others will require that you cite the source correctly. In this case you will need to state the owner/creator as well as the type of license used. See below “Using Wikicommons”. 4. Create your own images. You may choose to create your own diagrams or modify images using programs such as Adobe Photoshop or Adobe Fireworks. This is usually a more complicated option for using graphics, but can be mastered fairly quickly. For further information examine the DEC resource: Copyright for Teachers.
0 Comments
What is E-learning? E-learning is supporting learning through electronic (online) material. Students are able to access resources anytime and any place as long as they have access to the internet. E-learning can involve students accessing digital resources in class, just at home, or a combination of both. It can include videos, audio, interactive websites, online forums as well as text and images. It can incorporate mobile devices (phones, ipads, tablets). How could we use E-learning? - Subject – specific resources - Cross-curriculum projects - Welfare/Wellbeing resources - Library resources - Professional Learning for staff - Online courses/information for parents What are the issues related to introducing E-learning? - Staff training - Staff time and enthusiasm - Copyright issues - images, music, video, diagrams, etc - Quality control - Student access - across devices, using DEC internet - Marketing the school - Maintaining a competitive edge (seniors) - some people may be reluctant to share their senior resources. There are a range of options that can be used to introduce E-learning: - Moodle - iPads/Apps - Youtube - Gaming - Edmodo - Weebly/wordpress,etc
This is part two of a series of posts about the BYOD Project.
Teacher Surveys All teachers involved in the BYOD Project participated in BYOD Pre-Project Teacher survey. The key findings were:
Student Focus Groups Engaging with an academic partner during our action research journey enabled us to get guidance and feedback for a research methodology, it also provide insight into emerging research and introduced innovative practice to be implemented in the classroom. Dr Jane Hunter is from UWS, where she works in the areas of curriculum, pedagogy and technology integration in learning. She came to the school on in May to run two focus groups with 8-10 of our boys regarding technology use in the classroom. The sessions were audio-recorded, transcribed and then a report outlining the main themes was written. This provided pre-project data and information to provide direction for the project. Topics discussed include weaknesses and strengths in use of technology for learning currently, the use of technology to assist in: collaboration, creativity, problem solving, critical thinking, etc, the use of technology for sharing work with the outside world/community, differences between the technology skills students use at home and the skills they are “allowed”/expected to use at school, infrastructure/systems issues that make using technology difficult at school, opportunities/possibilities that students see in using technology – ideas, programs, strategies, processes, the value of technology to future employment and student perceptions of staff technology skills as compared to their own. Pre-Project Lesson Collection The last part of the pre-project phase was the collection of a couple of lesson plans outlining ways that technology is currently integrated into lessons. Following the submission of the lesson teachers met to discuss them with reference to some of the research and professional reading we had been looking at. A few samples of lesson plan proformas from the University of Sydney were emailed to teachers to use to write lesson plans.
The project was explained to teachers as an opportunity to identify an issues impacting education, undertake some basic research into the issues and different approaches to it, develop strategies to address it and to implement the strategies. A rough plan for the year was set out, and the philosophy of the approach was explored.
Teachers were provided with a range of different levels of involvement that they could opt into, so that they could choose to whether they just wanted to be kept informed, or to be an integral part of the project. Over the next year or so the Middle School Team at Epping Boys High School will be undertaking action research on the implementation of BYOD and teacher capacity to implement it effectively. It will be run with a small group of volunteer teachers with strategies implemented in some of their classes.
This Action Research Project aims to investigate the factors influencing the implementation of the BYOD program at Epping Boys High. It will examine the extent to which students are currently engaging with the program and students’ attitudes to BYOD. Teachers’ perceptions of the program will also be examined in addition to teachers’ technology capabilities and the pedagogical frameworks underpinning the integration of technology in the classroom. The aims of the project are to develop teacher capabilities in integrating technology in teaching practice with an emphasis on more collaborative, creative and productive uses of technology to enhance student learning. Teachers involved in the project will receive ongoing professional development and support. The project will involve ongoing documentation and mapping against the Australian Professional Standards to assist teachers in the accreditation process. Project Plan The project will be developed in three main phases: pre-project, project, and post-project. Pre-project Phase – collection of baseline data Before the commencement of the project baseline data will be collected including student and staff surveys and BYOD usage statistics. In this phase teachers involved will be asked to submit 2-3 lesson plans explaining how they have used the BYO Devices in the previous month or so. Student focus groups will be run. Project phase – implementation of professional learning and new skills Staff will undertake a range of professional learning experiences and collaboratively develop ideas and plans for integrating new technology skills into their teaching practice. The lesson ideas will be implemented across a number of classes across Years 7-9. Teachers will meet to reflect on their experiences and review their lesson ideas. Teachers will be asked to submit a further 2-3 lesson plans. Teachers may choose to observe each others’ lessons or team-teach to explore levels of student engagement. Post-project Phase – evaluation of project The post-project phase involves re-surveying of students and staff, collection of BYOD usage statistics, and collaborative assessment of lesson plans and reflection on the successes and failures of the project. This phase may bring to light further areas for development in future projects or initiatives. Relevant Research Some suggestions: Bloom's Digital Taxonomy High Possibility Classrooms: a new model of technology integration for schools Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge: A Framework for Teacher Knowledge Mobile Technologies and Learning literature review http://acec2014.acce.edu.au/sites/2014/files/ACEC2014%20Conference%20Proceedings%20Last.pdf http://www.futurelab.org.uk/resources As part of the BYOD Project a visit to Microsoft took place to explore solutions and strategies for us to use with our students.
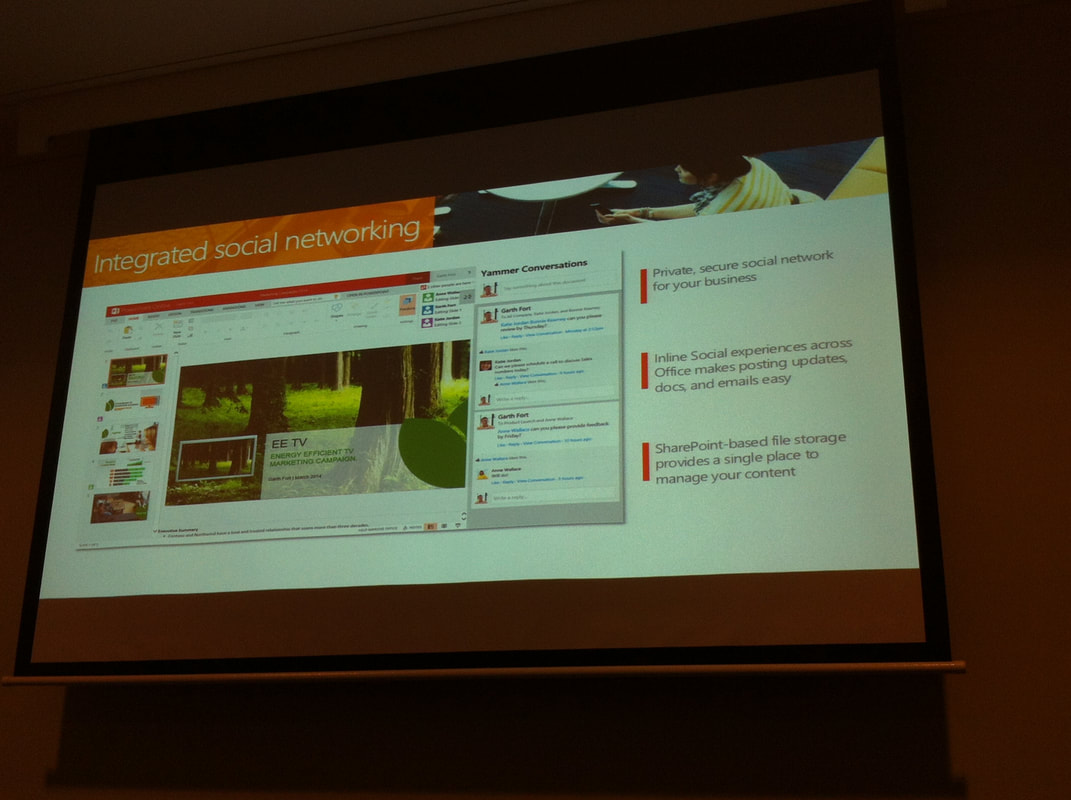
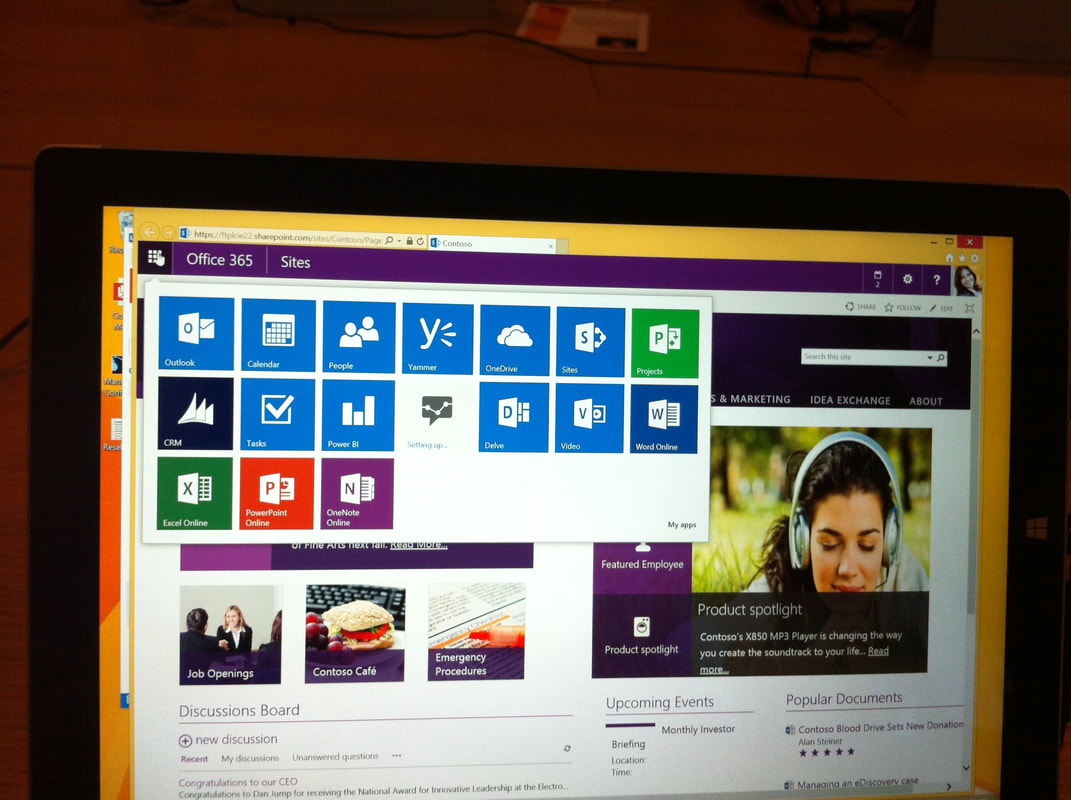
Teachers working on the BYOD Project engaged with external educational and technological professionals from Microsoft Head Office and InSynch to further develop professional knowledge and practice in relation to the implementation of Microsoft 365 in school. As a team, teachers explored the ways in which new software programs could be used to develop knowledge, skills, problem solving and critical and creative thinking in students. Teachers experimented with new software programs, and collaboratively assessed the effectiveness of these programs in supporting students’ understanding, engagement and achievement. Teachers participated in professional learning to further update their skills and to address targeted technology priorities in the school and the DEC as a whole. As a team, teachers fostered professional networks between Epping Boys High, Microsoft and partner companies with the intention to improve teaching and learning. |
Categories
All
Archives
April 2024
|