|
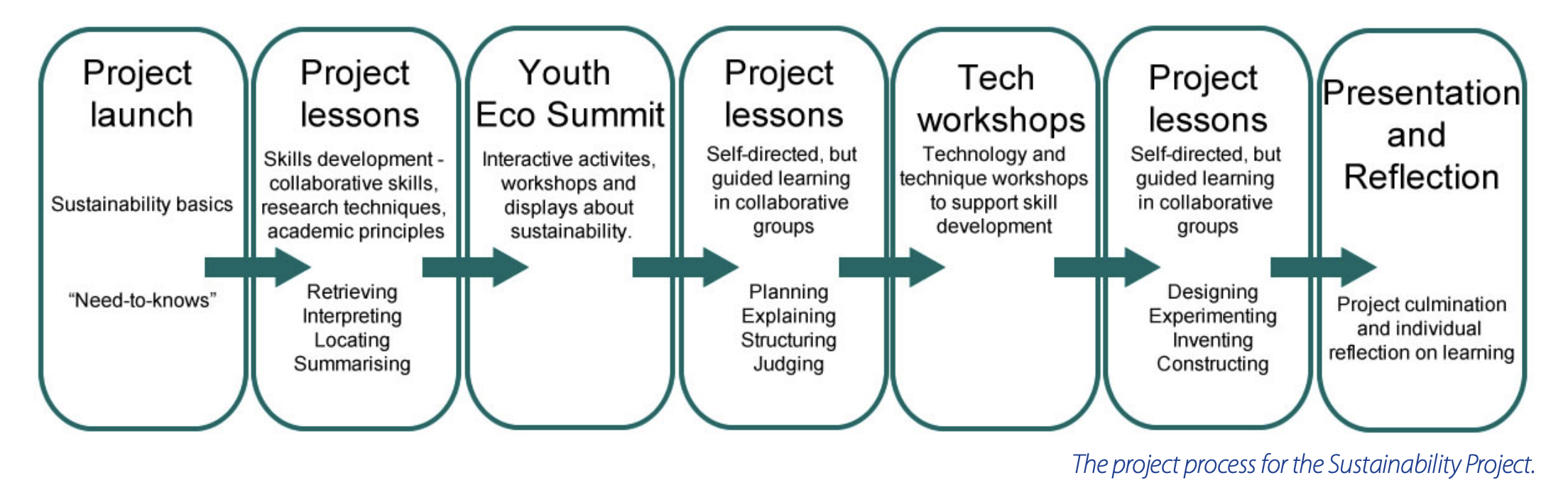
This is one of a series of posts on the Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project. Other posts in the series include: Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project (CCP) - Intro Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project - Research Techniques Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project - Evaluation Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project - Use augmented reality Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project - Create a multi-level game Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project - Create a sustainability video Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project - Build a sustainability app Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project - Design a sustainability city or town Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project - Overview For a more student-friendly layout visit the Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project website. The Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project was a compulsory task for all students in Year 7 at Epping Boys High School in Term 2014. It was facilitated by project lessons once a fortnight as well as several days of activities supporting learning about sustainability and the technology tools that would help students to complete the project. The project was completed in small groups of between 3 and 5. Students had a choice of how to present their projects. These choices are outlined below. • Design a city or town showing how you could incorporate a range of different sustainable technologies and techniques that would maintain a growing population for 50 years. • Create a 5 minute video about sustainability in the Epping community. • Create an app to teach the community about sustainable practices they can implement in their home. • Create a multi-level game that explores the consequences of not using sustainable practices in the Epping community. • Develop a visual representation of a sustainable design using a graphics program. Import the graphic into augmented reality software to represent the design in a suitable location, or to augment the information in certain contexts. A project website was designed to provide students with additional resources and explanations and links to tutorials. Projects skills development: Academic Principles, Collaborative Learning, Thinking and Research skills Students began the project by discussing the importance of being a good group member. The group structure was a valuable aspect of the project and supported the school’s student welfare program. Boys were encouraged to work collaboratively with their peers, participate fully in group discussions and practice conflict resolution techniques in managing their group. Creative thinking skills were modeled in the whole class setting, and in the presentation of the project to students, by way of using different techniques to brainstorm ideas, categorise and present information. Research techniques were examined including how to source quality information, use different search engines and summarise information. Students were provided with research scaffolds to begin recording information from their reading about their chosen topic. Referencing, citing sources and plagiarism were discussed and students were given access to referencing guides, videos and referencing scaffolds to support their project. After the students were taught each section of relevant information they were asked to apply their knowledge to the development of the project. In doing so, they gradually developed their project throughout the term in an academically rigorous, but supported way. Youth Eco Summit Students attended the Youth Eco Summit, an annual event organised by Sydney Olympic Park, the Department of Education and Communities and the University of Western Sydney. The timing of the Sustainability Project in Term 4 was intended to take advantage of this event. The festival-style event provided students with the opportunity to attend workshops, engage with interactive displays, participate in seminars and watch student presentations. All of the activities focused on environmental, cultural and economic sustainability. The event included video conferencing opportunities for remote schools. It also used this technology to provide students with access to experts from around the globe through interviews and web chats. Environmental Education Centres, universities and community organisations ran stalls and workshops on topics such as solar cars, bicycle power generation, composting and waste management. The day was organised to allow groups to attend up to three pre-booked workshops. This allowed flexibility and choice for groups to explore the myriad activities that were scheduled across the venue. The workshops engaged the students in hands-on, interactive activities, and emphasised the real world, practical application of student learning about sustainability. In the lead up to the Youth Eco Summit professional learning sessions were run at Sydney Olympic Park to increase teacher capacity in delivering content related to sustainability. Project development: Scaffolding the project creation process A project creation process was replicated across each of the five project options to ensure that students developed their ideas in a logical sequence. Students examined and reviewed existing examples of their chosen end-product, for example existing games or videos about sustainability. They then brainstormed their own ideas for the creation of an original product. Students were provided with basic scaffolds to plan the creation of the project including relevant subject content. Links to relevant tutorials, videos and online resources were provided to allow students to further develop their skills and knowledge. See examples of research scaffolds provided to students on pages 32 and 33. Examples of scaffolds to assist the creation stage of the project. Technology and technique workshops Students spent a day attending technology and technique workshops to provide them with some of the technical skills to be able to complete their project. Staff from a variety of faculties volunteered their time to run the workshops. The technology sessions included Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Premiere and app design. A group of Year 10 students also led the students through the use of digital game design using Kudo with the assistance of a teacher. Technique workshops included sessions on dramatic techniques and model building. These sessions were important to develop essential skills in students to become, “…creative and productive users of technology, especially ICT…” ,(p8, MCEETYA, 2008), and to ensure that any existing deficiencies in technology would not hinder the creation of the project. Presentation and reflection Students presented their projects in front of a class of their peers in the school auditorium. Students used websites such as appmakr.com, appypie.com and iBuildapp to create app prototypes. Many of the students used the skills they had developed in the technology workshops to create sustainability games in kodu. SketchUp was most commonly used to create a city model. Several groups created high quality videos. Interestingly, none of the groups chose to present their project as augmented reality. Augmented reality is where a student is able to present a computer-generated image so that it appears to be placed in the real world. This is usually done using apps such as Aurasma. This may reflect the need for additional support in understanding and mastering augmented reality apps. Students were required to present a written report to make a judgement on how sustainable their community is at present, and how their project would contribute to its sustainability into the future. It was in this section of the project that evidence of cross curriculum thinking was most evident. Students were expected to explicitly state the links between their chosen subjects, sustainability and their project end-products. Students chose to present their evaluations in a variety of forms such as Prezi, PowerPoint, oral presentations and written report. Students were given a set of questions to guide a reflection on their learning. Many students described issues with working within a group structure, time management and workload. They also indicated a deep understanding of the concept of sustainability and its relevance in a range of contexts. Project rationale The rationale for the project was to provide an alternative methodology to the traditional secondary pedagogic model, where concepts are taught in subjects often with limited connections to other fields of study. In line with the Melbourne Declaration on Educational Goals for Young Australians (MCEETYA, 2008) and the Department of Education and Communities’ Middle Years Transition Matrix there was a desire to develop cross curricular thinking and an ability to solve problems by drawing on a range of disciplines. It is also a way of meaningfully incorporating principles of 21st century learning, and facilitating professional dialogue across faculties about the Australian Curriculum’s Cross Curriculum Priorities. This project aimed to foster collaborative and inquiry-based learning, to encourage social activity and cohesion between classes, and to give students the opportunity to extend themselves and explore their own interests. The project was the first implementation of this concept across a whole year group at Epping Boys High School. Why Sustainability? The topic of the project was selected from the Cross Curriculum Priorities developed by ACARA for the Australian Curriculum and adopted by the BOSTES in the new NSW syllabuses. For 2014 the topic of sustainability needed to be incorporated into all the Phase 1 subjects for implementation (Math, English, History and Science). As the new syllabuses are released for the Phase 2 and 3 subjects, sustainability will also need to be incorporated. The Department of Education and Communities’ NSW Policy, Implementing the Environmental Education Policy in your schools (2001) has previously provided a framework for and specified methods of integrating environmental sustainability in teaching across the curriculum. For this project the subjects that are addressed are Science, Geography, Timber, Metal, Drama and Technology. The topic of sustainability provided a great platform for a project to have real world application. The main inquiry question for the Sustainability Project was “How can we make our community more sustainable?”. This enabled students to engage with issues and developments at a range of scales from their immediate community to national and global contexts. It also provided a pathway for students to become more informed citizens who are actively engaged with their community. Why implement a Cross Curriculum Project? The Melbourne Declaration on Educational Goals for Young Australians determines a nationally consistent direction for Australian schools and provides guiding principles to shape future planning. One of the key ideas of the declaration is enhancing middle years development by giving students the opportunity to move across subject areas in the development of new expertise and the ability to solve problems that draw upon a range of learning areas and disciplines (MCEETYA, 2008). The Sustainability Project incorporated subject content and skills from a range of Key Learning Areas as well as several of the General Capabilities identified by ACARA and adopted by BOSTES. Students were asked to explicitly integrate content from two subjects chosen from TAS, Geography and Science, however depending on choice end-products also incorporated Technology and Drama. Students were required to demonstrate literacy skills in the two pieces of written work to accompany the project. Students were provided with a Wordle (examples are provided next to each subject) and a list of modified, relevant syllabus content for each subject (TAS, Geography and Science) from Stage 4 syllabuses. This was a means to spark student thinking, to encourage connections between subjects and to provide the opportunity for students to choose topics of most interest. For Science, the new BOSTES syllabus incorporating the Australian Curriculum was used. In Geography content was drawn from the existing BOSTES syllabus, but some content from the draft new BOSTES syllabus was also used. For TAS, the existing BOSTES syllabus was used. The implication of this is that if the project is to be used again in the future it will need to evolve to transition to all new syllabuses as they are released. The suggested content related to Geography includes introductory concepts related to sustainability such as the importance of physical environments (air, flora and fauna, soils, solar energy and water), the operation of ecosystems, and renewable, non-renewable and continuous resources. Content from the existing Geography syllabus includes the interaction between human and physical environments, and the way humans, including indigenous groups, interact with the environment. Content that has been incorporated from the draft BOSTES Geography syllabus includes the availability of fresh water resources, potential sources of freshwater, and the environmental, social and economic effects of water movement as it connects places. Possible Science content includes how people use a variety of natural and made resources, rating strategies used by people to conserve and manage non-renewable resources, and evaluating different viewpoints people may have in making decisions about the use of a major non-renewable source found in Australia. The TAS (Metal and Timber) courses mirror each other in the way they deal with sustainability. Relevant content includes issues related to sustainability in the metal/timber industry, examples of renewable and non-renewable resources in the timber/metal industry, the role of recycling in metal/timber industries, and the effects of the metal/timber industry on the environment. The project incorporates several of the General Capabilities developed by ACARA and adopted by BOSTES including critical and creative thinking, ethical understanding, information and communication technology (ICT) capability, literacy and personal and social capability. The project requires students to critically analyse and draw conclusions about the sustainability of their community and evaluate how their project contributes to sustainability. Students employed creative thinking by generating original ways to encourage or address sustainability, refining their ideas, and producing end-products in a variety of formats such as video, digital games, augmented reality, models or apps. The topic of sustainability inherently requires students to undertake ethical judgments regarding issues of resource allocation, fairness, equity and the actions of individuals and groups. The project structure also incorporated ethical understanding related to academic principles and research techniques. Collaborative use of ICT was used for the purpose of creating and presenting solutions to complex problems. A formal literacy activity was included as one of the supporting documents to be handed in with the project. This was scaffolded and explicitly explained to provide support for students requiring learning support including EAL/D students. Personal and social capability was addressed by the project in the fact that students had to work in groups and manage themselves and their relationships with their peers to bring the project to fruition. Students needed to communicate, collaborate and negotiate in order to navigate the project. Teachers led a class of approximately 30 students, or seven groups. The teachers were selected to provide a range of cross-disciplinary expertise and as such came from a range of faculties. Additional teachers provided support through the provision of technology and technique workshops. Throughout the various stages of the project faculties represented included Social Science, Science, CAPA, TAS, PDHPE, and Math. Student grouping Epping Boys High School has classes in Year 7 roughly streamed. One class is selected by way of the submission of a portfolio and is intended for students who are gifted and talented across a range of areas. One class is selected based on academic performance only and four classes are generally mixed. One of the mixed classes has a small number of students requiring learning and support and another has students requiring EAL/D support. There are also a small number of Year 7 students in the school’s Autism unit who took part in the program. The Melbourne Declaration provides guidance on the types of learning to be encouraged, and the skills to be developed in students. It outlines that students should develop the ability to plan activities independently, collaborate in teams, and develop the capacity to work with others (MCEETYA, 2008). For the Sustainability Cross Curriculum Project students were grouped heterogeneously, including students from a range of classes and with a variety of abilities and skills. The intention behind this was to best support the learning and social development of all students (Hayes Jacobs, 2010) and to vary the loose ability groupings to address any “…negative social-emotional impacts…” (p143, Whitten et al, 2009) of the current class structures. Each group contained a student from one of the gifted and talented classes. These students had completed a Cross Curriculum Project of their own choice earlier in the year and had been involved in programs specifically designed to foster critical and creative thinking and problem solving skills. These students acted as group mentors and leaders. The study of sustainability requires students to actively engage in real world problems, is futures focused, and inspires students to find ecologically and socially just solutions. As such it is an inherently positive learning experience, empowering students with the knowledge of how to shape their community.
0 Comments
|
Categories
All
Archives
April 2024
|